| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2018-05-02 10:42:44 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2018-05-04 14:28:32 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC001146 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB011930 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | 2,3-Butanedione |
|---|
| Description | Constituent of butter; formed during fermentation. A common constituent of plant oils, production of breakdown of carbohydrates. Flavouring additive used in food industryand is also present in apple, orange, plum, okra, walnut, Bourbon vanilla, clary sage, soybean, coffee, honey, rose wine, port wine, cocoa and scallop
Beer sometimes undergoes a diacetyl rest, in which its temperature is raised slightly for two or three days after fermentation is complete, to allow the yeast to absorb the diacetyl it produced earlier in the fermentation cycle. The makers of some wines, such as chardonnay, deliberately promote the production of diacetyl because of the feel and flavor it imparts. It is present in many California chardonnays known as "Butter Bombs," although there is a growing trend back toward the more traditional French styles.[citation needed]; Diacetyl (IUPAC systematic name: butanedione or 2,3-butanedione) is a natural byproduct of fermentation. It is a vicinal diketone (two C=O groups, side-by-side) with the molecular formula C4H6O2. Diacetyl occurs naturally in alcoholic beverages and is added to some foods to impart a buttery flavor.; Diacetyl is a natural by-product of secondary or malolactic fermentation. It is a vicinal diketone (two C=O groups, side-by-side) with the molecular formula C4H6O2.; Carrier of aroma of butter, vinegar, coffee, and other foods.; Beer sometimes undergoes a diacetyl rest, which entails waiting two or three days after fermentation is complete, to allow the yeast to absorb the diacetyl it produced earlier in the fermentation cycle. The makers of some wines, such as chardonnay, deliberately promote the production of diacetyl because of the feel and flavors it imparts. 2,3-Butanedione is found in many foods, some of which are capers, linden, sweet marjoram, and brazil nut. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 431-03-8 |
|---|
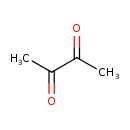
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (CH3CO)2 | biospider | | 2,3 Butandione (Diacetyl) | biospider | | 2,3 Butanedione | biospider | | 2,3-Butadione | biospider | | 2,3-Butandione | biospider | | 2,3-Butanedione (8CI,9CI) | biospider | | 2,3-butanedione (diacetal) | biospider | | 2,3-Butanedione (Diacetyl) | biospider | | 2,3-butanodione | biospider | | 2,3-Diketobutane | biospider | | 2,3-Dioxobutane | biospider | | Acetoacetaldehyde | biospider | | Biacetyl | db_source | | buta-2,3-dione | biospider | | Butadione | biospider | | Butan-2,3-dione | biospider | | Butan-2,3-dione (diacetyl) | biospider | | Butanal, 3-oxo- | biospider | | Butane-2,3-dione | biospider | | Butane-2,3-dione (diacetyl) | biospider | | Butanedione | biospider | | Butanedione (diacetyl) | biospider | | Butanedione [UN2346] | biospider | | Butanedione [UN2346] [Flammable liquid] | biospider | | Diacetyl | db_source | | Diketobutane | biospider | | Dimethyl diketone | db_source | | Dimethyl glyoxal | biospider | | Dimethyldiketone | biospider | | Dimethylglyoxal | biospider | | Dotriacontane | biospider | | FEMA 2370 | db_source | | Glyoxal, dimethyl- | biospider |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H6O2 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | butane-2,3-dione |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H6O2/c1-3(5)4(2)6/h1-2H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | QSJXEFYPDANLFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CC(=O)C(C)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 86.0892 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 86.036779436 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha-diketones. These are organic compounds containing two ketone groups on two adjacent carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbonyl compounds |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha-diketones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-diketone
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | -1.34 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 200 mg/mL at 15 oC | YALKOWSKY,SH & HE,Y (2003) |
|---|
| Melting Point | Fp 7° | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | 1 to 2 ml |
|---|
| Delivery Time | 2 weeks |
|---|
| Storage Form | liquid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | 4°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | unknown |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
| Contact Name | Contact Institution | Contact Email |
|---|
| Augustin Scalbert | International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Biomarkers Group, 150 cours Albert Thomas, Lyon, FR, 69372 | scalberta@iarc.fr |
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | B690030 |
|---|