| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:33:28 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:42 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000937 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB023933 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | D-Aspartic acid |
|---|
| Description | D-Aspartic acid is the D-isomer of aspartic acid. Since its discovery in invertebrates, free D-aspartate (D-Asp) has been identified in a variety of organisms, including microorganisms, plants, and lower animals, mammals and humans. D-Asp in mammalian tissues is present in specific cells, indicating the existence of specific molecular components that regulate D-Asp levels and localization in tissues. In the rat adrenal medulla, D-Asp is closely associated with adrenaline-cells (A-cells), which account for approximately 80% of the total number of chromaffin cells in the tissue, and which make and store adrenaline. D-Asp appears to be absent from noradrenaline-cells (NA-cells), which comprise approximately 20% of the total number of chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla, and which make and store noradrenaline. D-aspartate oxidase (EC 1.4.3.1, D-AspO), which catalyzes oxidative deamination of D-Asp, appears to be present only in NA-cells, suggesting that the lack of D-Asp in these cells is due to D-Asp oxidase-mediated metabolism of D-Aspecies In the rat adrenal cortex, the distribution of D-Asp changes during development. It has been suggested that developmental changes in the localization of D-Asp reflects the participation of D-Asp in the development and maturation of steroidogenesis in rat adrenal cortical cells. D-Asp is involved in steroid hormone synthesis and secretion in mammals as well. D-Asp is synthesized intracellularly, most likely by Asp racemase (EC 5.1.1.13). Endogenous D-Asp apparently has two different intracellular localization patterns: cytoplasmic and vesicular. D-Asp release can occur through three distinct pathways: 1) spontaneous, continuous release of cytoplasmic D-Asp, which is not associated with a specific stimulus; 2) release of cytoplasmic D-Asp via a volume-sensitive organic anion channel that connects the cytoplasm and extracellular space; 3) exocytotic discharge of vesicular D-Aspecies D-Asp can be released via a mechanism that involves the L-Glu transporter. D-Asp is thus apparently in dynamic flux at the cellular level to carry out its physiological function(s) in mammals. (PMID: 16755369) [HMDB] |
|---|
| CAS Number | 1783-96-6 |
|---|
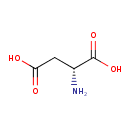
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (-)-Aspartic acid | hmdb | | (2R)-2-Aminobutanedioate | hmdb | | (2R)-2-Aminobutanedioic acid | hmdb | | (R)-2-Aminobutanedioate | hmdb | | (R)-2-Aminobutanedioic acid | hmdb | | (R)-2-Aminosuccinic acid | hmdb | | (R)-Aspartic acid | hmdb | | 1-Amino-1,2-carboxyethane | hmdb | | Aspartate D-form | Generator | | aspartic acid | hmdb | | Aspartic acid D-form | ChEBI | | D-(-)-Aspartic acid | hmdb | | D-Asparaginsaeure | hmdb | | D-aspartate | hmdb | | D-aspartic acid | hmdb | | delta-(-)-Aspartic acid | hmdb | | delta-asparaginsaeure | hmdb | | delta-aspartate | hmdb | | delta-aspartic acid | hmdb | | Lopac-alpha-9256 | hmdb | | Tocris-0213 | hmdb |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H7NO4 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | (2R)-2-aminobutanedioic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-UWTATZPHSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 133.1027 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 133.037507717 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as aspartic acid and derivatives. Aspartic acid and derivatives are compounds containing an aspartic acid or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of aspartic acid at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Aspartic acid and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Aspartic acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid
- D-alpha-amino acid
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Fatty acid
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 1 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | G147 |
|---|
| AKSci | HMDB0006483 |
|---|
| Glentham | GM2767 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0006483 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | A790020 |
|---|