| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:33:12 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:40 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000882 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB000455 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Theobromine |
|---|
| Description | Theobromine, also known as diurobromine, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as xanthines. These are purine derivatives with a ketone group conjugated at carbons 2 and 6 of the purine moiety. Theobromine is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Theobromine is an isomer of theophylline, as well as paraxanthine. Theobromine exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. Within humans, theobromine participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, theobromine and formaldehyde can be biosynthesized from caffeine through the action of the enzymes cytochrome P450 1A2 and cytochrome P450 2E1. In addition, theobromine can be converted into 3,7-dimethyluric acid through its interaction with the enzyme xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase. In humans, theobromine is involved in caffeine metabolism. Theobromine is a bitter tasting compound. Outside of the human body, Theobromine is found, on average, in the highest concentration within a few different foods, such as cocoa powders, chocolates, and cocoa beans and in a lower concentration in other candies, cakes, and soy milks. Theobromine has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as hyacinth beans, oyster mushrooms, tamarinds, milk (other mammals), and watercress. This could make theobromine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Theobromine and caffeine are similar in that they are related alkaloids. A necropsy and toxicology report performed at the University of New Hampshire in 2015 confirmed they died of heart failure caused by theobromine after they consumed 41 kilograms (90 lb) of chocolate and doughnuts placed at the site as bait. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 83-67-0 |
|---|
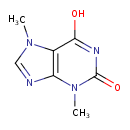
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3, 7-dihydro-3,7-dimethyl- | biospider | | 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-3,7-dimethyl- | biospider | | 1H-purine-2,6-dione,3,7-dihydro-3,7- dimethyl- (9CI) | biospider | | 2,6-Dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-purine | biospider | | 2,6-Dihydroxy-3,7-dimethylpurine | biospider | | 3-7-DIMETHYLXANTHINE | biospider | | 3,7-Dihydro-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione | biospider | | 3,7-Dihydro-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione, 9CI | db_source | | 3,7-Dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione | biospider | | 3,7-Dimethyl-xanthine | biospider | | 3,7-dimethylpurine-2,6-dione | biospider | | 3,7-Dimethylxanthine | db_source | | Diurobromine | db_source | | FEMA 3591 | db_source | | Santheose | db_source | | Teobromin | biospider | | Theobromin | biospider | | Theobromine [ban] | biospider | | Theobrominum | biospider | | Theosalvose | biospider | | Theostene | biospider | | Thesal | db_source | | Thesodate | biospider | | Xanthine, 3,7-dimethyl- | biospider |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C7H8N4O2 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 3,7-dimethyl-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C7H8N4O2/c1-10-3-8-5-4(10)6(12)9-7(13)11(5)2/h3H,1-2H3,(H,9,12,13) |
|---|
| InChI Key | YAPQBXQYLJRXSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CN1C=NC2=C1C(=O)NC(=O)N2C |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 180.164 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 180.06472552 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as xanthines. These are purine derivatives with a ketone group conjugated at carbons 2 and 6 of the purine moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Imidazopyrimidines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Purines and purine derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Xanthines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Xanthine
- 6-oxopurine
- Purinone
- Alkaloid or derivatives
- Pyrimidone
- N-substituted imidazole
- Pyrimidine
- Azole
- Imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Vinylogous amide
- Lactam
- Urea
- Azacycle
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | -0.78 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 0.33 mg/mL at 25 oC | YALKOWSKY,SH & HE,Y (2003) |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 351° | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 1 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | J10550 |
|---|
| AKSci | Q815 |
|---|
| AKSci | HMDB0002825 |
|---|
| Cayman Chemical | 21745 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0002825 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | T343800 |
|---|