| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:33:11 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:40 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000878 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB023163 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | D-Lysine |
|---|
| Description | Lysine and its bioactive form L-lysine, abbreviated Lys or L, is an essential amino acid. Normal requirements for adults are between 8 g per day or 12 mg/kg. Children and infants need more: 44 mg/kg per day for an eleven to-twelve-year old, and 97 mg/kg per day for three-to six-month old. Lysine is highly concentrated in muscle compared to most other amino acids. Normal lysine metabolism is dependent upon many nutrients including niacin, vitamin B6, riboflavin, vitamin C, glutamic acid and iron. Several inborn errors of lysine metabolism are known, such as cystinuria, hyperdibasic aminoaciduria I, lysinuric protein intolerance, propionic acidemia, and tyrosinemia I. Most are marked by mental retardation with occasional diverse symptoms such as absence of secondary sex characteristics, undescended testes, abnormal facial structure, anemia, obesity, enlarged liver and spleen, and eye muscle imbalance. Low lysine levels have been found in patients with Parkinson's, hypothyroidism, kidney disease, asthma and depression. The exact significance of these levels is unclear, yet lysine therapy can normalize these levels and has been associated with improvement of some patients with these conditions. Abnormally elevated hydroxylysines have been found in virtually all chronic degenerative diseases and coumadin therapy. The levels of this stress marker may be improved by high doses of vitamin C. Lysine is particularly useful in therapy for marasmus (wasting) and herpes simplex. It stops the growth of herpes simplex in culture and has helped to reduce the number and occurrence of cold sores in clinical studies. Beneficial clinical effects occurred with lysine doses ranging from 100 mg to 4 g a day. Higher doses may also be useful, and toxicity has not been reported in doses as high as 8 g per day. Diets high in lysine and low in arginine can be useful in the prevention and treatment of herpes as excess arginine antagonizes lysine. Lysine also may be a useful adjunct in the treatment of osteoporosis because it reduces calcium losses in urine. Although high protein diets result in loss of large amounts of calcium in urine, so does lysine deficiency. Lysine deficiency also may result in immunodeficiency. Requirements for this amino acid are probably increased by stress. Lysine is high in foods such as wheat germ, cottage cheese, chicken, wild game and pork. Less lysine is found in apple, apricot, bananas, avocados, guava, lime, brazil nuts, cashews, mung bean, fava bean and black bean as well as other seeds, nuts and fruits. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 923-27-3 |
|---|
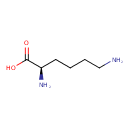
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (R)-2,6-Diaminohexanoate | Generator | | (R)-2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid | ChEBI | | D-2,6-Diaminohexanoate | hmdb | | D-2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid | hmdb | | D-Lysin | ChEBI |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H14N2O2 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | (2R)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H14N2O2/c7-4-2-1-3-5(8)6(9)10/h5H,1-4,7-8H2,(H,9,10)/t5-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | KDXKERNSBIXSRK-RXMQYKEDSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 146.19 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 146.105527699 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as d-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the D-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | D-alpha-amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - D-alpha-amino acid
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Amino fatty acid
- Fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Amino acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 500 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | K683 |
|---|
| Glentham | GM3691 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | L468930 |
|---|