| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:33:10 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:39 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000870 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB023167 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | D-Arginine |
|---|
| Description | Arginine is an essential amino acid that is physiologically active in the L-form. In mammals, arginine is formally classified as a semi-essential or conditionally essential amino acid, depending on the developmental stage and health status of the individual. Infants are unable to effectively synthesize arginine, making it nutritionally essential for infants. Adults, however, are able to synthesize arginine in the urea cycle. Arginine can be considered to be a basic amino acid as the part of the side chain nearest to the backbone is long, carbon-containing, and hydrophobic, whereas the end of the side chain is a complex guanidinium group. With a pKa of 12.48, the guanidinium group is positively charged in neutral, acidic, and even most basic environments. Because of the conjugation between the double bond and the nitrogen lone pairs, the positive charge is delocalized. This group is able to form multiple H-bonds. L-Arginine is an amino acid that has numerous functions in the body. It helps dispose of ammonia, is used to make compounds such as nitric oxide, creatine, L-glutamate, and L-proline, and it can be converted into glucose and glycogen if needed. In large doses, L-arginine also stimulates the release of the hormones growth hormone and prolactin. Arginine is a known inducer of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) and is responsible for inducing protein synthesis through the mTOR pathway. mTOR inhibition by rapamycin partially reduces arginine-induced protein synthesis (PMID: 20841502). Catabolic disease states such as sepsis, injury, and cancer cause an increase in arginine utilization, which can exceed normal body production, leading to arginine depletion. Arginine also activates AMP kinase (AMPK) which then stimulates skeletal muscle fatty acid oxidation and muscle glucose uptake, thereby increasing insulin secretion by pancreatic beta-cells (PMID: 21311355). Arginine is found in plant and animal proteins, such as dairy products, meat, poultry, fish, and nuts. The ratio of L-arginine to lysine is also important: soy and other plant proteins have more L-arginine than animal sources of protein. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 157-06-2 |
|---|
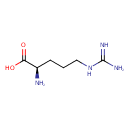
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (2R)-2-amino-5-(Carbamimidamido)pentanoate | Generator | | (2R)-2-amino-5-(Carbamimidamido)pentanoic acid | ChEBI | | (2R)-2-amino-5-Guanidinopentanoate | Generator | | (2R)-2-amino-5-Guanidinopentanoic acid | ChEBI | | (R)-2-amino-5-Guanidinopentanoate | Generator | | (R)-2-amino-5-Guanidinopentanoic acid | ChEBI | | D-2-Amino-5-guanidinovalerate | hmdb | | D-2-Amino-5-guanidinovaleric acid | hmdb | | D-Arginin | ChEBI |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H14N4O2 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | (2R)-2-amino-5-carbamimidamidopentanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H14N4O2/c7-4(5(11)12)2-1-3-10-6(8)9/h4H,1-3,7H2,(H,11,12)(H4,8,9,10)/t4-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-SCSAIBSYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | N[C@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 174.201 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 174.111675712 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as d-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the D-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | D-alpha-amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - D-alpha-amino acid
- Fatty acid
- Guanidine
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboximidamide
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 30 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | E162 |
|---|
| AKSci | J91868 |
|---|
| Glentham | GM7267 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | A769515 |
|---|