| Description | Venlafaxine is an effective antidepressant for many persons; Venlafaxine is a bicyclic antidepressant, and is usually categorized as a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), but it has been referred to as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor. It works by blocking the transporter reuptake proteins for key neurotransmitters affecting mood, thereby leaving more active neurotransmitter in the synapse. The neurotransmitters affected are serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Additionally, in high doses it weakly inhibits the reuptake of dopamine; A comparison of adverse event rates in a fixed dose study comparing venlafaxine 75, 225, and 375 mg/day with placebo revealed a dose dependency for some of the more common adverse events associated with venlafaxine use. The rule for including events was to enumerate those that occurred at an incidence of 5% or more for at least one of the venlafaxine groups and for which the incidence was at least twice the placebo incidence for at least one venlafaxine group. Tests for potential dose relationships for these events (Cochran-Armitage Test, with a criterion of exact 2-sided p-value <= 0.05) suggested a dose-dependency for several adverse events in this list, including chills, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, agitation, dizziness, somnolence, tremor, yawning, sweating, and abnormal ejaculation.[Wyeth Monograph]; Venlafaxine is an effective anti-depressant for many persons; however, it seems to be especially effective for those with treatment resistant depression. Some of these persons have taken two or more antidepressants prior to venlafaxine with no relief. Patients suffering with severe long-term depression typically respond better to venlafaxine than other drugs. However, venlafaxine has been reported to be more difficult to discontinue than other antidepressants. In addition, a September 2004 Consumer Reports study ranked venlafaxine as the most effective among six commonly prescribed antidepressants. However, this should not be considered a definitive finding, since responses to psychiatric medications can vary significantly from individual to individual; however, it seems to be especially effective for those with treatment-resistant depression. Some of these persons have taken two or more antidepressants prior to venlafaxine with no relief. Patients suffering with severe long term depression typically respond better to venlafaxine than other drugs. However, venlafaxine has been reported to be more difficult to discontinue than other antidepressants. In addition, a September 2004 Consumer Reports study ranked venlafaxine as the most effective among six commonly prescribed antidepressants. However, this should not be considered a definitive finding, since responses to psychiatric medications can vary significantly from individual to individual; Venlafaxine hydrochloride is a prescription antidepressant that belongs to the class of antidepressants called serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI).
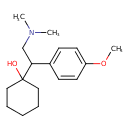
The chemical structure of venlafaxine is designated (R/S)-1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4 methoxyphenyl)ethyl] cyclohexanol hydrochloride or (+/-)-1-[alpha [alpha- (dimethylamino)methyl] p-methoxybenzyl] cyclohexanol hydrochloride and it has the empirical formula of C17H27NO2. It is a white to off-white crystalline solid. Venlafaxine is structurally and pharmacologically related to the analgesic tramadol, but not to any of the conventional antidepressant drugs, including tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs, MAOIs, or reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (RIMAs); A Black Box Warning has been issued with Effexor and with other SSRI and SNRI anti-depressants advising of risk of suicide. Thoughts of suicide (suicide ideation) as potential risk of suicide as shown in studies by Wyeth and reported on their datasheet for effexor were twice that of placebo (4% compared to 2%, however, no suicides occurred in these trials). The black box warnings advise physicians to carefully monitor patients for suicide risk at start of usage and whenever the dosage is changed. There is an additional risk if a physician misinterprets patient expression of adverse effects such as panic or akithesia. Careful assessment of patient history and comorbid risk factors such as drug abuse are essential in evaluating the safety of Effexor for individual patients. These cautions are emphasized in Wyeth's detailed information sheet with special precautions if prescribed to children. The extent of this effect and the actual risk are not known as studies may exclude individuals with higher risk. This is another reason why careful patient monitoring at start of use of this medication, as well as at any change of dosage is emphasized. Another risk is Serotonin syndrome. This is a serious effect that can be caused by interactions with other drugs and is potentially fatal. This risk necessitates clear information to patients and proper medical history. For example, the drug abuse by at risk patients of certain non-prescription drugs can cause this serious effect and emphasizes the importance of good medical history sharing between General Practitioners and Psychiatrists as both may prescribe Venlafaxine. Involvement of family in awareness of risk factors is highlighted in Wyeth information sheets on Effexor; The chemical structure of venlafaxine is designated (R/S)-1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4 methoxyphenyl)ethyl] cyclohexanol hydrochloride or (+/-)-1-[alpha [alpha- (dimethylamino)methyl] p-methoxybenzyl] cyclohexanol hydrochloride and it has the empirical formula of C17H27NO2. It is a white to off-white crystalline solid. Venlafaxine is structurally and pharmacologically related to the analgesic tramadol, but not to any of the conventional antidepressant drugs, including tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs, MAOIs, or reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (RIMAs); Venlafaxine is used primarily for the treatment of depression, generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder in adults. It is also used for other general depressive disorders. Although it is not approved for use in children or adolescents, there is a considerable information by Wyeth on cautions if presecribed to this age group. Venlafaxine hydrochloride is a prescription antidepressant first introduced by Wyeth in 1993. It belongs to class of antidepressants called serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI). As of August 2006, generic venlafaxine is available in the United States. It was previously available only under the brand names Effexor and Effexor XR. [HMDB] |
|---|