| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:32:55 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:37 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000822 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB022617 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Phosphate |
|---|
| Description | Phosphate (Pi) is an essential component of life. In classical endocrine regulation, low serum phosphate induces the renal production of the seco-steroid hormone 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3).This active metabolite of vitamin D acts to restore circulating mineral levels by increasing absorption in the intestine, reabsorption in the kidney, and mobilization of calcium and phosphate from bone. Thus, chronic renal failure is associated with hyperparathyroidism, which in turn contributes to osteomalacia. Another complication of chronic renal failure is hyperphosphatemia.
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) has recently been recognized as a key mediator of phosphate homeostasis, its most notable effect being promotion of phosphate excretion. FGF-23 was discovered to be involved in diseases such as autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets, X-linked hypophosphatemia, and tumor-induced osteomalacia in which phosphate wasting was coupled to inappropriately low levels of 1,25(OH)2D3. FGF-23 is regulated by dietary phosphate in humans: phosphate restriction decreased FGF-23, and phosphate loading increased FGF-23.
Phosphate must be actively transported into cells against its electrochemical gradient. In vertebrates, two unrelated families of Na+-dependent Pi transporters carry out this task. Remarkably, the two families transport different Pi species: whereas type II Na+/Pi cotransporters (SCL34) prefer divalent HPO4(2), type III Na+/Pi cotransporters (SLC20) transport monovalent H2PO4. The SCL34 family comprises both electrogenic and electroneutral members that are expressed in various epithelia and other polarized cells. Through regulated activity in apical membranes of the gut and kidney, they maintain body Pi homeostasis, and in salivary and mammary glands, liver, and testes they play a role in modulating the Pi content of luminal fluids.
Hyperphosphatemia is a prevalent condition in the dialysis population and is associated with increased risk of mortality. Hypophosphatemia (hungry bone syndrome) has been associated to postoperative electrolyte aberrations and after parathyroidectomy. (PMID: 17581921, 11169009, 11039261, 9159312, 17625581) [HMDB]. Phosphate is found in many foods, some of which are yellow zucchini, avocado, longan, and garden rhubarb. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 14265-44-2 |
|---|
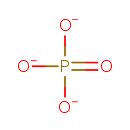
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| [PO4](3-) | ChEBI | | ate (PO43-) | HMDB | | ate Anion(3-) | HMDB | | ate Ion (PO43-) | HMDB | | ate Ion(3-) | HMDB | | ate Trianion | HMDB | | ate(3-) | HMDB | | ic acid ION | Generator | | NFB orthoate | HMDB | | NFB Orthophosphate | hmdb | | O-Oric acid | HMDB | | Oric acid ion(3-) | HMDB | | ortho-ate | HMDB | | Ortho-phosphate | hmdb | | orthoate (PO43-) | HMDB | | orthoate(3-) | HMDB | | Orthophosphate (PO43-) | hmdb | | Orthophosphate(3-) | hmdb | | Phosphate | hmdb | | Phosphate (PO43-) | hmdb | | Phosphate anion(3-) | hmdb | | Phosphate ion (PO43-) | hmdb | | Phosphate ion(3-) | hmdb | | Phosphate trianion | hmdb | | Phosphate(3-) | hmdb | | Phosphoric acid ion(3-) | hmdb | | Pi | hmdb | | PO4(3-) | ChEBI |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | O4P |
|---|
| IUPAC name | phosphate |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/H3O4P/c1-5(2,3)4/h(H3,1,2,3,4)/p-3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 94.9714 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 94.95342 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as non-metal phosphates. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds containing a phosphate as its largest oxoanion. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds |
|---|
| Class | Non-metal oxoanionic compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Non-metal phosphates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Non-metal phosphates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Non-metal phosphate
- Inorganic oxide
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Not Available |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 1 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Not Available |