| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:32:32 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:35 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000758 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB012156 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | L-Selenomethionine |
|---|
| Description | Found in onion, cabbage, coco de mono (Lecythis elliptica), Brazil nuts (Bertholletia excelsa), wheat grains and other plants. Dietary supplement for avoidance of Se deficiency in humans and ruminants
It has been suggested that selenomethionine, which is an organic form of selenium, is easier for the human body to absorb than selenite, which is an inorganic form. It was determined in a clinical trial that selenomethionine is absorbed 19% better than selenite.; Selenomethionine is an amino acid containing selenium that cannot be synthesized by higher animals, but can be obtained from plant material. Selenomethionine is the major seleno-compound in cereal grains (wheat grain, maize and rice), soybeans and enriched yeast. Seleno-compounds present in plants may have a profound effect upon the health of animals and human subjects. It is now known that the total Se content cannot be used as an indication of its efficacy, but knowledge of individual selenocompounds is necessary to fully assess the significance. Thus, speciation of the seleno-compounds has moved to the forefront. Since animals and man are dependent upon plants for their nutritional requirements, this makes the types of seleno-compounds in plants even more critical. Se enters the food chain through incorporation into plant proteins, mostly as selenocysteine and selenomethionine at normal Se levels. There are two possible pathways for the catabolism of selenomethionine. One is the transsulfuration pathway via selenocystathionine to produce selenocysteine, which in turn is degraded to H2Se by the enzyme b-lyase. The other pathway is the transamination-decarboxylation pathway. It was estimated that 90% of methionine is metabolized through this pathway and thus could be also the major route for selenomethionine catabolism. (PMID: 14748935, Br J Nutr. 2004 Jan;91(1):11-28.); Selenomethionine is an amino acid containing selenium. The L-isomer of selenomethionine, known as Se-met and Sem, is a common natural food source of selenium. In vivo, selenomethionine is randomly incorporated instead of methionine and is readily oxidized. Its antioxidant activity arises from its ability to deplete reactive species. Selenium and sulfur are chalcogen elements that share many chemical properties and the substitution of methionine to selenomethionine may have no effect on protein structure and function. However, the incorporation of selenomethionine into tissue proteins and keratin in horses causes alkali disease. Alkali disease is characterized by emaciation, loss of hair, deformation and shedding of hooves, loss of vitality and erosion of the joints of long bones. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 3211-76-5 |
|---|
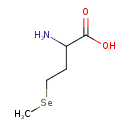
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (+-)-Selenomethionine | ChEBI | | (2S)-2-amino-4-(methylseleno)Butanoate | HMDB | | (2S)-2-amino-4-(methylseleno)Butanoic acid | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-4-(methylseleno)-Butanoate | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-4-(methylseleno)-Butanoic acid | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-4-(methylseleno)Butanoate | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-4-(methylseleno)Butanoic acid | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-4-(methylseleno)Butyric acid | HMDB | | 2-amino-4-(methylseleno)Butanoate | HMDB | | 2-amino-4-(methylseleno)Butanoic acid | HMDB | | 2-amino-4-(Methylselenyl)butyrate | HMDB | | 2-amino-4-(Methylselenyl)butyric acid | HMDB | | DL-Selenomethionine | HMDB | | L-2-amino-4-(Methylselenyl)-butyric acid | HMDB | | L-Selenomethioninum | HMDB | | L(+)-Selenomethionine | HMDB | | MSE | HMDB | | Selenium methionine | ChEBI | | Selenium-L-methionine | HMDB | | Seleno-D,L-methionine | HMDB | | Seleno-DL-methionine | ChEBI | | Seleno-L-methionine | HMDB | | Selenomethionine se 75 | HMDB | | Selenomethionine; L-form | db_source | | SeMet | HMDB | | Sethotope | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C5H11NO2Se |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 2-amino-4-(methylselanyl)butanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C5H11NO2Se/c1-9-3-2-4(6)5(7)8/h4H,2-3,6H2,1H3,(H,7,8) |
|---|
| InChI Key | RJFAYQIBOAGBLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | C[Se]CCC(N)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 196.11 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 196.995500429 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-amino acid
- Fatty acid
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Selenoether
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Primary amine
- Organoselenium compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | 275 oC | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 50 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Not Available |