| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:32:30 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:35 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000752 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB000633 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Kaempferol |
|---|
| Description | Kaempferol, also known as rhamnolutein or c.i. 75640, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as flavonols. Flavonols are compounds that contain a flavone (2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one) backbone carrying a hydroxyl group at the 3-position. Thus, kaempferol is a flavonoid lipid molecule. Kaempferol is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble in water, and relatively neutral. Kaempferol is a bitter tasting compound. It is very widespread in the plant world and is found in Brassicaceae, Apocynaceae, Dilleniaceae, Ranunculaceae and Leguminosae. It is detected in apples, tomatoes, green tea, potatoes, onions, brussels sprouts, squash, cucumbers, lettuce, green beans, peaches, blackberries, raspberries, spinach, grapes, broccoli, capers, chives, kale, garden cress, fennel, lovage, dill weed and tarragon (PMID: 21428901). Kaempferol is a biomarker for the consumption of dried and cooked beans. Many glycosides of kaempferol, such as kaempferitrin and astragalin, have been isolated as natural products from plants. Kaempferol consumption in tea and broccoli has been associated with reduced risk of heart disease. Kaempferol has numerous protective properties and has been used to treat intervertebral disc degeneration and colitis, post-menopausal bone loss, acute lung injury and has beneficial effects against cancer, liver injury, obesity and diabetes, and inhibits vascular endothelial inflammation. These treatments and protective properties of kaempferol and the potential mechanisms that kaempferol exerts these effects are part of this review ( PMID: 31572524). |
|---|
| CAS Number | 520-18-3 |
|---|
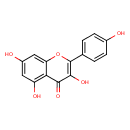
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| 3,4',5,7-Tetrahydroxy-flavone (7ci,8ci) | HMDB | | 3,4',5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone | biospider | | 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | HMDB | | 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, 9CI | db_source | | 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one | biospider | | 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | biospider | | 3,5,7,4'-Tetrahydroxyflavone | biospider | | 4',5,7-Trihydroxyflavonol | db_source | | 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavonol | ChEBI | | 5,7,4'-Trihydroxyflavonol | biospider | | C.I. 75640 | ChEBI | | Campherol | db_source | | Indigo yellow | ChEBI | | Kaemferol | biospider | | Kaempferol | db_source | | Kaempherol | biospider | | Kampcetin | biospider | | Kampferol | biospider | | Kampherol | db_source | | Kempferol | biospider | | Nimbecetin | db_source | | Pelargidenolon | biospider | | Pelargidenon | biospider | | Populnetin | db_source | | Rhamnolutein | biospider | | Rhamnolutin | db_source | | Robigenin | db_source | | Swartziol | db_source | | Trifolitin | db_source |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C15H10O6 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C15H10O6/c16-8-3-1-7(2-4-8)15-14(20)13(19)12-10(18)5-9(17)6-11(12)21-15/h1-6,16-18,20H |
|---|
| InChI Key | IYRMWMYZSQPJKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | OC1=CC=C(C=C1)C1=C(O)C(=O)C2=C(O1)C=C(O)C=C2O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 286.2363 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 286.047738052 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as flavonols. Flavonols are compounds that contain a flavone (2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one) backbone carrying a hydroxyl group at the 3-position. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Phenylpropanoids and polyketides |
|---|
| Class | Flavonoids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Flavones |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Flavonols |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 3-hydroxyflavone
- 3-hydroxyflavonoid
- 4'-hydroxyflavonoid
- 5-hydroxyflavonoid
- 7-hydroxyflavonoid
- Hydroxyflavonoid
- Chromone
- Benzopyran
- 1-benzopyran
- 1-hydroxy-4-unsubstituted benzenoid
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Phenol
- Pyranone
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Pyran
- Benzenoid
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Vinylogous acid
- Polyol
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Oxacycle
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 276-278° | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 40 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | 2157AH |
|---|
| AKSci | C554 |
|---|
| AKSci | J10449 |
|---|
| Cayman Chemical | 11852 |
|---|
| Glentham | GP7425 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | K100000 |
|---|