| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:31:44 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:31 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000641 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB022665 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Phosphocreatine |
|---|
| Description | Phosphocreatine undergoes irreversible cyclization and dehydration to form creatinine at a fractional rate of 0.026 per day, thus forming approximately 2 g creatinine/day in an adult male. This is the amount of creatine that must be provided either from dietary sources or by endogenous synthesis to maintain the body pool of (creatine and) phosphocreatine. Creatine is an amino acid that plays a vital role as phosphocreatine in regenerating adenosine triphosphate in skeletal muscle to energize muscle contraction. Creatine is phosphorylated to phosphocreatine in muscle in a reaction that is catalyzed by the enzyme creatine kinase. This enzyme is in highest concentration in muscle and nerve. Oral administration increases muscle stores. During the past decade, creatine has assumed prominence as an ergogenic (and legal) aid for professional and elite athletes. Most (~ 95%) of the total body creatine-phosphocreatine pool is in muscle (more in skeletal muscle than in smooth muscle) and amounts to 120 g (or 925 mmol) in a 70 kg adult male. Approximately 60-67% of the content in resting muscle is in the phosphorylated form. This generates enough ATP at the myofibrillar apparatus to power about 4 seconds of muscle contraction in exercise. Phosphocreatine reacts with ADP to yield ATP and creatine; the reversible reaction is catalyzed by creatine kinase. phosphocreatine is the chief store of high-energy phosphates in muscle. Thus, this reaction, which permits the rephosphorylation of ADP to ATP, is the immediate source of energy in muscle contraction. During rest, metabolic processes regenerate phosphocreatine stores. In normal muscle, ATP that is broken down to ADP is immediately rephosphorylated to ATP. Thus, phosphocreatine serves as a reservoir of ATP-synthesizing potential. phosphocreatine is the only fuel available to precipitously regenerate ATP during episodes of rapid fluctuations in demand. The availability of phosphocreatine likely limits muscle performance during brief, high-power exercise, i.e., maximal exercise of short duration. With near maximal isometric contraction, the rate of utilization of phosphocreatine declines after 1-2 seconds of contraction, prior to the glycolysis peak at approximately 3 seconds. (PMID: 10079702, Nutr Rev. 1999 Feb;57(2):45-50.) [HMDB] |
|---|
| CAS Number | 67-07-2 |
|---|
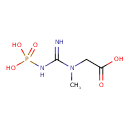
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| {[imino(onoamino)methyl](methyl)amino}acetate | Generator | | {[imino(onoamino)methyl](methyl)amino}acetic acid | ChEBI | | Creatine ate | ChEBI | | Creatine ic acid | ChEBI | | Creatine phosphate | hmdb | | Creatine phosphic acid | hmdb | | Creatine-ate | HMDB | | creatine-P | hmdb | | creatine-phosphate | hmdb | | Creatineoric acid | HMDB | | Creatinephosphoric acid | hmdb | | N-(N-Onoamido)sarcosine | ChEBI | | N-(Onoamidino)-sarcosine | HMDB | | N-(Onoamidino)sarcosine | ChEBI | | N-(phosphonoamidino)-Sarcosine | hmdb | | N-(Phosphonoamidino)sarcosine | hmdb | | N-[Imino(onoamino)methyl]-N-methyl-glycine | HMDB | | N-[imino(phosphonoamino)methyl]-N-methyl-Glycine | hmdb | | N-Ocreatine | ChEBI | | N-Orocreatine | HMDB | | N-Orylcreatine | ChEBI | | N-phosphocreatine | hmdb | | N-Phosphorocreatine | hmdb | | N-Phosphorylcreatine | hmdb | | N(Omega)-onocreatine | ChEBI | | neo-ton | hmdb | | Ocreatine | ChEBI | | Orylcreatine | ChEBI | | P-creatine | hmdb | | phosphocreatine | hmdb | | phosphorylcreatine | hmdb |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H10N3O5P |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 2-(N-methyl-N'-phosphonocarbamimidamido)acetic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H10N3O5P/c1-7(2-3(8)9)4(5)6-13(10,11)12/h2H2,1H3,(H,8,9)(H4,5,6,10,11,12) |
|---|
| InChI Key | DRBBFCLWYRJSJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CN(CC(O)=O)C(=N)NP(O)(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 211.1131 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 211.035806957 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids and derivatives. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon), or a derivative thereof. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Guanidine
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 400 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | F341 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | P354600 |
|---|