| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:31:32 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:30 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000618 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | L-Dehydroascorbic acid |
|---|
| Description | Widespread in plants, as oxidn. production of Ascorbic acid BWR05-S. Formed reversibly in vivo from ascorbic acid and shows similar vitamin function
Dehydroascorbic acid (DHA) is an oxidized form of ascorbic acid. It is actively imported into the endoplasmic reticulum of cells and generates the oxidative potential found there. Protein disulfide isomerases are known to reduce DHA back to ascorbic acid, oxidizing their disulfide bonds in the process. Therefore L-dehydroascorbic acid is a vitamin C compound much like L-ascorbic acid. Oxidized forms of esterified ascorbic acids can be numbered at C(5) or C(6) atoms and the (free) chemical radical semi-dehydroascorbate or semidehydro ascorbic acid (SDA) to the group of dehydroascorbic acids.; Dehydroascorbic acid is the oxidized form of vitamin C. Reduced Vitamin C concentrations in the brain exceed those in blood by 10 fold. Dehydroascorbic acid readily enters the brain and is retained in the brain tissue in the form of ascorbic acid (ascorbic acid is not able to cross the blood-brain barrier).; Therefore, transport of dehydroascorbic acid by the Glucose Transporter 1 (GLUT1, Glucose transporters are integral membrane glycoproteins involved in transporting glucose into most cells. GLUT1 is a major glucose transporter in the mammalian blood-brain barrier. It is present at high levels in primate erythrocytes and brain endothelial cells.) is a mechanism by which the brain acquires vitamin C. (OMIM 138140); Vitamin C does not pass from the blood stream into the brain, although the brain is one of the organs which has the greatest concentration of vitamin C. Instead it is dehydroascorbate that is transported through the blood-brain barrier via GLUT1 transporters, and then converted to vitamin C. Some research has suggested that administration of dehydroascorbic acid may confer protection from neuronal injury following an ischemic stroke. L-Dehydroascorbic acid is found in many foods, some of which are whisky, nutmeg, pepper (spice), and wild celery. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 490-83-5 |
|---|
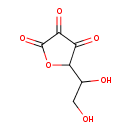
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| 1-Dehydroascorbate | biospider | | 1-Dehydroascorbic acid | biospider | | Dehydro-l-ascorbate | biospider | | Dehydro-l-ascorbic acid | biospider | | Dehydroascorbate | biospider | | Dehydroascorbic acid | biospider | | DHAA | biospider | | L-ascorbic acid, dehydro- | biospider | | L-dehydroascorbate | biospider | | L-dehydroascorbic acid | biospider | | L-threo-2,3-Hexodiulosonic acid gamma-lactone | biospider | | L-threo-2,3-Hexodiulosonic acid, gamma-lactone | biospider | | L-Threo-hexo-2,3-diulosono-1,4-lactone | biospider | | Oxidized ascorbate | biospider | | Oxidized ascorbic acid | biospider | | Oxidized vitamin c | biospider |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC name | Not Available |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H6O6/c7-1-2(8)5-3(9)4(10)6(11)12-5/h2,5,7-8H,1H2 |
|---|
| InChI Key | SBJKKFFYIZUCET-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | OCC(O)C1OC(=O)C(=O)C1=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 174.1082 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 174.016437924 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as gamma butyrolactones. Gamma butyrolactones are compounds containing a gamma butyrolactone moiety, which consists of an aliphatic five-member ring with four carbon atoms, one oxygen atom, and bears a ketone group on the carbon adjacent to the oxygen atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Lactones |
|---|
| Sub Class | Gamma butyrolactones |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Gamma butyrolactones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 3-furanone
- Gamma butyrolactone
- Tetrahydrofuran
- 1,2-diol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Cyclic ketone
- Secondary alcohol
- Ketone
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Primary alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 225 dec. (196° dec.) | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 100 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | X2154 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0001264 |
|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | HMDB0001264 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | D229250 |
|---|