| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:31:18 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:27 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000549 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB022758 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Pseudoephedrine |
|---|
| Description | Pseudoephedrine (commonly abbreviated as PSE) is a sympathomimetic amine commonly used as a decongestant. The salts pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine sulfate are found in many over-the-counter preparations either as single ingredient preparations, or more commonly in combination with antihistamines, paracetamol and/or ibuprofen. Consumers often refer to it by a product which contains pseudoephedrine, such as Sudafed, the trademark for a common brand of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride in North America; Pseudoephedrine is a phenethylamine, and an isomer of ephedrine. Pseudoephedrine is the International Nonproprietary Name (INN) of the (1S,2S)- diastereomer of ephedrine (which has 1R,2S- configuration). Other names are (+)-pseudoephedrine and D-pseudoephedrine. (Reynolds, 1989) (-)-(1R,2R)-Pseudoephedrine is not used clinically, since it is associated with greater central nervous system (CNS) stimulatory effects. (+)-(1S,2S)-Pseudoephedrine is a less-potent CNS stimulant, yet it retains its efficacy as a decongestant. -- Wikipedia; Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine - that is, its principal mechanism of action relies on its indirect action on the adrenergic receptor system. While it may have weak agonist activity at adrenergic receptors, the principal mechanism is to displace noradrenaline from storage vesicles in presynaptic neurons. The displaced noradrenaline is released into the neuronal synapse where it is free to activate the aforementioned postsynaptic adrenergic receptors. -- Wikipedia; Pseudoephedrine is a phenethylamine, and an isomer of ephedrine. Pseudoephedrine is the International Nonproprietary Name (INN) of the (1S,2S)- diastereomer of ephedrine (which has 1R,2S- configuration). Other names are (+)-pseudoephedrine and D-pseudoephedrine (Reynolds, 1989). The enantiomer (-)-(1R,2R)-Pseudoephedrine has fewer side-effects, fewer central nervous system (CNS) stimulatory effects, does not reduce to d-methamphetamine, yet retains its efficacy as a decongestant.[citation needed] However, the patent holder for (-)-Pseudoephedrine (Pfizer/Warner-Lambert) has not yet sought or received government approval for its sale to the public.(US Patent 6,495,529); Treatment for urinary incontinence is an unlabeled use for these medications. Unlabeled use means doctors can use the medication to treat a condition other than that for which it was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These medications are approved by the FDA for the treatment of nasal congestion caused by colds or allergies. However it has also been succesful in treating stress incontinence by increasing the pressure (tension) exerted by the muscles of the bladder neck and the urethra, which helps retain the urine within the bladder; An alpha and beta adrenergic agonist that may also enhance release of norepinephrine. It has been used in the treatment of several disorders including asthma, heart failure, rhinitis, and urinary incontinence, and for its central nervous system stimulatory effects in the treatment of narcolepsy and depression. It has become less extensively used with the advent of more selective agonists; Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine commonly used as a decongestant. The salts pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine sulfate are found in many over-the-counter preparations either as single-ingredient preparations, or more commonly in combination with antihistamines, paracetamol and/or ibuprofen. It is often referred to by consumers as Sudafed, which is the trademark for a common brand of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride. -- Wikipedia; Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine - that is, its principal mechanism of action relies on its indirect action on the adrenergic receptor system. While it may have weak agonist activity at alpha and beta adrenergic receptors, the principal mechanism is to displace noradrenaline from storage vesicles in presynaptic neurons. The displaced noradrenaline is released into the neuronal synapse where it is free to activate the aforementioned postsynaptic adrenergic receptors. [HMDB] |
|---|
| CAS Number | 90-82-4 |
|---|
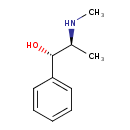
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (+)-(1S,2S)-Pseudoephedrine | hmdb | | (+)-Pseudoephedrine | hmdb | | (+)-psi-Ephedrine | hmdb | | (+)-threo-Ephedrine | hmdb | | (1S,2S)-(+)-Pseudoephedrine | hmdb | | (1S,2S)-Pseudoephedrine | hmdb | | 1-ephedrine | hmdb | | 2-(Methylamino)-1-phenyl-1-propanol | hmdb | | Besan | hmdb | | D-isoephedrine | hmdb | | D-pseudoephedrine | hmdb | | d-Pseudoephedrine base | hmdb | | d-psi-2-Methylamino-1-phenyl-1-propanol | hmdb | | D-psi-Ephedrine | hmdb | | Isoephedrine | hmdb | | L-(+)-Pseudoephedrine | hmdb | | L(+)-psi-Ephedrine | hmdb | | Novafed | hmdb | | Pseudoefedrina | hmdb | | Pseudoephedrine | hmdb | | Pseudoephedrine d-form | hmdb | | Pseudoephedrine Ephedrine | hmdb | | Pseudoephedrinum | hmdb | | Psi-ephedrin | hmdb | | Psi-ephedrine | ChEBI | | Sudafed | hmdb | | trans-Ephedrine | hmdb |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C10H15NO |
|---|
| IUPAC name | (1S,2S)-2-(methylamino)-1-phenylpropan-1-ol |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C10H15NO/c1-8(11-2)10(12)9-6-4-3-5-7-9/h3-8,10-12H,1-2H3/t8-,10+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | KWGRBVOPPLSCSI-WCBMZHEXSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CN[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 165.2322 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 165.115364107 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenylpropanes. These are organic compounds containing a phenylpropane moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
|---|
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Phenylpropanes |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Phenylpropanes |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Phenylpropane
- Aralkylamine
- 1,2-aminoalcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Secondary aliphatic amine
- Secondary amine
- Alcohol
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 1 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | P839340 |
|---|