| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:31:17 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:27 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000544 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB021801 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | 3-Oxobutanoic acid, 9CI |
|---|
| Description | It is a weak organic acid and can be produced in the human liver under certain conditions of poor metabolism leading to excessive fatty acid breakdown (diabetes mellitus leading to diabetic ketoacidosis), it is then partially converted to acetone by decarboxylation and excreted either in urine or through respiration. Persistent mild hyperketonemia is a common finding in newborns. These compounds serve as an indispensable source of energy for extrahepatic tissues, especially the brain and lung of developing rats. Another important function of ketone bodies is to provide acetoacetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA for synthesis of cholesterol, fatty acids, and complex lipids. During the early postnatal period, acetoacetate (AcAc) and beta-hydroxybutyrate are preferred over glucose as substrates for synthesis of phospholipids and sphingolipids in accord with requirements for brain growth and myelination. Thus, during the first 2 wk of postnatal development, when the accumulation of cholesterol and phospholipids accelerates, the proportion of ketone bodies incorporated into these lipids increases. On the other hand, an increased proportion of ketone bodies are utilized for cerebroside synthesis during the period of active myelination. In the lung, AcAc serves better than glucose as a precursor for the synthesis of lung phospholipids. The synthesized lipids, particularly dipalmityl phosphatidylcholine, are incorporated into surfactant, and thus have a potential role in supplying adequate surfactant lipids to maintain lung function during the early days of life. (PMID 3884391) The acid is also present in the metabolism of those undergoing starvation or prolonged physical exertion as part of gluconeogenesis. When ketone bodies are measured by way of urine concentration, acetoacetic acid, along with beta-hydroxybutyric acid or acetone, is what is detected. [HMDB] |
|---|
| CAS Number | 541-50-4 |
|---|
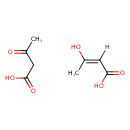
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| 3-Ketobutanoate | Generator | | 3-Ketobutanoic acid | ChEBI | | 3-Ketobutyrate | Generator | | 3-Ketobutyric acid | ChEBI | | 3-Oxobutyrate | Generator | | 3-Oxobutyric acid | ChEBI | | Acetoacetate | Generator | | Acetoacetic acid | db_source | | Acetonecarboxylic acid | db_source | | Acetylacetic acid | db_source | | b-Ketobutyrate | Generator | | b-Ketobutyric acid | Generator | | beta-Ketobutyrate | Generator | | beta-Ketobutyric acid | ChEBI | | Diacetate | HMDB | | Diacetic acid | db_source | | β-ketobutyrate | Generator | | β-ketobutyric acid | Generator |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H12O6 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | (2E)-3-hydroxybut-2-enoic acid; 3-oxobutanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/2C4H6O3/c2*1-3(5)2-4(6)7/h2H2,1H3,(H,6,7);2,5H,1H3,(H,6,7)/b;3-2+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | UNNIHLXYGZEWRE-ZPYUXNTASA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CC(=O)CC(O)=O.C\C(O)=C/C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 204.1773 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 204.063388116 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as short-chain keto acids and derivatives. These are keto acids with an alkyl chain the contains less than 6 carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Short-chain keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Short-chain keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Short-chain keto acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Beta-keto acid
- Fatty acyl
- Fatty acid
- 1,3-dicarbonyl compound
- Unsaturated fatty acid
- Beta-hydroxy ketone
- Vinylogous acid
- Ketone
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Enol
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Not Available |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 60 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Not Available |