| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:31:09 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:27 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000526 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB000569 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Aspartame |
|---|
| Description | Compd. with 100 times the sweetness of sucrose. Artificial sweetener permitted in foods in EU at 300-5500 ppmand is also permitted in USA. Widely used in foods, beverages and pharmaceutical formulations
Aspartame (L-alpha-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester) is a low-calorie sweetener used to sweeten a wide variety of low- and reduced-calorie foods and beverages, including low-calorie tabletop sweeteners. Aspartame is composed of two amino acids, aspartic acid and phenylalanine, as the methyl ester. Aspartic acid and phenylalanine are also found naturally in protein containing foods, including meats, grains and dairy products. Methyl esters are also found naturally in many foods such as fruits and vegetable and their juices. Upon digestion, aspartame breaks down into three components (aspartic acid, phenylalanine and methanol), which are then absorbed into the blood and used in normal body processes. Neither aspartame nor its components accumulates in the body. These components are used in the body in the same ways as when they are derived from common foods.; Aspartame is an artificial sweetener. It is 200 times sweeter than sugar in typical concentrations, without the high energy value of sugar. While aspartame, like other peptides, has a caloric value of 4 kilocalories (17 kilojoules) per gram, the quantity of aspartame needed to produce a sweet taste is so small that its caloric contribution is negligible, which makes it a popular sweetener for those trying to avoid calories from sugar. The taste of aspartame is not identical to that of sugar: the sweetness of aspartame has a slower onset and longer duration than that of sugar. Blends of aspartame with acesulfame potassium?usually listed in ingredients as acesulfame K?are alleged[who?] to taste more like sugar, and to be sweeter than either substitute used alone.; Aspartame is the name for an artificial, non-carbohydrate sweetener, aspartyl-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester; This sweetener is marketed under a number of trademark names, including Equal, NutraSweet, and Canderel, and is an ingredient of approximately 6,000 consumer foods and beverages sold worldwide, including (but not limited to) diet sodas and other soft drinks, instant breakfasts, breath mints, cereals, sugar-free chewing gum, cocoa mixes, frozen desserts, gelatin desserts, juices, laxatives, chewable vitamins supplements, milk drinks, pharmaceutical drugs and supplements, shake mixes, tabletop sweeteners, teas, instant coffees, topping mixes, wine coolers and yogurt. It is provided as a table condiment in some countries. However, aspartame is not always suitable for baking because it often breaks down when heated and loses much of its sweetness. Aspartame is also one of the main sugar substitutes used by people with diabetes.; i.e., the methyl ester of the dipeptide of the amino acids aspartic acid and phenylalanine. It is marketed under a number of trademark names, such as Equal, and Canderel, and is an ingredient of approximately 6,000 consumer foods and beverages sold worldwide. It is commonly used in diet soft drinks, and is often provided as a table condiment. It is also used in some brands of chewable vitamin supplements. In the European Union, it is also known under the E number (additive code) E951. Aspartame is also one of the sugar substitutes used by diabetics. Upon ingestion, aspartame breaks down into several constituent chemicals, including the naturally-occurring essential amino acid phenylalanine which is a health hazard to the few people born with phenylketonuria, a congenital inability to process phenylalanine. Aspartic acid is an amino acid commonly found in foods. Approximately 40% of aspartame (by mass) is broken down into aspartic acid. Because aspartame is metabolized and absorbed very quickly (unlike aspartic acid-containing proteins in foods), it is known that aspartame could spike blood plasma levels of aspartate. Aspartic acid is in a class of chemicals known as excitotoxins. Abnormally high levels of excitotoxins have been shown in hundreds of animals studies to cause damage to areas of the brain unprotected by the blood-brain barrier and a variety of chronic diseases arising out of this neurotoxicity. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 22839-47-0 |
|---|
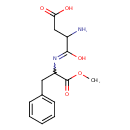
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| 1-Methyl N-L-a-aspartyl-L-phenylalanate | Generator | | 1-Methyl N-L-a-aspartyl-L-phenylalanic acid | Generator | | 1-Methyl N-L-alpha-aspartyl-L-phenylalanate | biospider | | 1-Methyl N-L-alpha-aspartyl-L-phenylalanic acid | Generator | | 1-Methyl N-L-alpha-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine | biospider | | 1-Methyl N-L-α-aspartyl-L-phenylalanate | Generator | | 1-Methyl N-L-α-aspartyl-L-phenylalanic acid | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(a-Carboxyphenethyl)succinamate N-methyl ester | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(a-Carboxyphenethyl)succinamic acid N-methyl ester | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(a-Methoxycarbonylphenethyl) succinamate | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(a-Methoxycarbonylphenethyl) succinamic acid | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(alpha-Carboxyphenethyl)succinamate N-methyl ester | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(alpha-Carboxyphenethyl)succinamic acid N-methyl ester | ChEBI | | 3-amino-N-(alpha-Methoxycarbonylphenethyl) succinamate | Generator | | 3-Amino-N-(alpha-methoxycarbonylphenethyl) succinamic acid | biospider | | 3-amino-N-(α-carboxyphenethyl)succinamate N-methyl ester | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(α-carboxyphenethyl)succinamic acid N-methyl ester | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(α-methoxycarbonylphenethyl) succinamate | Generator | | 3-amino-N-(α-methoxycarbonylphenethyl) succinamic acid | Generator | | a-APM | db_source | | APM | biospider | | Asp-phe-ome | biospider | | Aspartam | biospider | | Aspartame (NF/inn) | biospider | | Aspartame [usan:ban:inn] | biospider | | Aspartame, l,l-alpha- | biospider | | Aspartamo | biospider | | Aspartamum | biospider | | Aspartylphenylalanine methyl ester | biospider | | Canderel | db_source | | Dipeptide sweetener | biospider | | e 951 | HMDB | | E951 | db_source | | Equal | biospider | | L-Aspartyl-L-3-phenylalanine methyl ester | biospider | | L-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine methyl ester | biospider | | L-aspartyl-l-phenylalanyl methyl ester | biospider | | L-Phenylalanine, L-alpha-aspartyl-, 2-methyl ester | biospider | | L-Phenylalanine, N-L-alpha-aspartyl-, 1-methyl ester | biospider | | Methyl aspartylphenylalanate | biospider | | Methyl aspartylphenylalanine | db_source | | Methyl l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanate | biospider | | Methyl l-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine | biospider | | Methyl n-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalaninate | biospider | | N-a-Aspartyl-L-phenylalanine 1-methyl ester, 9CI | db_source | | N-L-alpha-Aspartyl-L-phenylalanine 1-methyl ester | biospider | | Nutrasweet | db_source | | Pal sweet | biospider | | Palsweet diet | biospider | | SC-18862 | db_source | | Sweet dipeptide | biospider | | Tri-sweet | biospider |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C14H18N2O5 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 3-amino-3-[(1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl)-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl]propanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C14H18N2O5/c1-21-14(20)11(7-9-5-3-2-4-6-9)16-13(19)10(15)8-12(17)18/h2-6,10-11H,7-8,15H2,1H3,(H,16,19)(H,17,18) |
|---|
| InChI Key | IAOZJIPTCAWIRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | COC(=O)C(CC1=CC=CC=C1)N=C(O)C(N)CC(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 294.3031 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 294.121571696 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as peptides. Peptides are compounds containing an amide derived from two or more amino carboxylic acid molecules (the same or different) by formation of a covalent bond from the carbonyl carbon of one to the nitrogen atom of another. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Peptides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha peptide
- Phenylalanine or derivatives
- Aspartic acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid ester
- N-acyl-alpha amino acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid amide
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Amphetamine or derivatives
- Fatty acid ester
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Fatty amide
- N-acyl-amine
- Fatty acyl
- Benzenoid
- Methyl ester
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carboxamide group
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 245-247° (double Mp) (235-236° dec.) | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 200 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | E436 |
|---|
| AKSci | J10514 |
|---|
| AKSci | HMDB0001894 |
|---|
| Glentham | GE0967 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0001894 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | A790015 |
|---|