| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:30:47 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:24 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000454 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB015780 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Squalene |
|---|
| Description | Squalene, also known as (e,e,e,e)-squalene or all-trans-squalene, is a member of the class of compounds known as triterpenoids. Triterpenoids are terpene molecules containing six isoprene units. Squalene can be found in a number of food items such as apricot, savoy cabbage, peach (variety), and bitter gourd, which makes squalene a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Squalene can be found primarily in blood, feces, and sweat, as well as throughout most human tissues. In humans, squalene is involved in several metabolic pathways, some of which include risedronate action pathway, steroid biosynthesis, alendronate action pathway, and fluvastatin action pathway. Squalene is also involved in several metabolic disorders, some of which include cholesteryl ester storage disease, CHILD syndrome, hyper-igd syndrome, and wolman disease. Squalene is a natural 30-carbon organic compound originally obtained for commercial purposes primarily from shark liver oil (hence its name, as Squalus is a genus of sharks), although plant sources (primarily vegetable oils) are now used as well, including amaranth seed, rice bran, wheat germ, and olives. Yeast cells have been genetically engineered to produce commercially useful quantities of "synthetic" squalene . |
|---|
| CAS Number | 7683-64-9 |
|---|
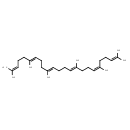
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| 2,6,10,15,19,23-Hexamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22-tetracosahexaene, 9CI | db_source | | Spinacene | db_source |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C30H50 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | (6Z,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyltetracosa-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C30H50/c1-25(2)15-11-19-29(7)23-13-21-27(5)17-9-10-18-28(6)22-14-24-30(8)20-12-16-26(3)4/h15-18,23-24H,9-14,19-22H2,1-8H3/b27-17+,28-18+,29-23-,30-24+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | YYGNTYWPHWGJRM-FLHYQJCXSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CC(C)=CCC\C(C)=C/CC\C(C)=C\CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CCC=C(C)C |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 410.718 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 410.3912516 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as triterpenoids. These are terpene molecules containing six isoprene units. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Triterpenoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Triterpenoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Triterpenoid
- Branched unsaturated hydrocarbon
- Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbon
- Unsaturated hydrocarbon
- Olefin
- Acyclic olefin
- Hydrocarbon
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 500 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Not Available |