| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:30:37 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:23 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000423 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB021829 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Levothyroxine |
|---|
| Description | The thyronamines function via some unknown mechanism to inhibit neuronal activity; this plays an important role in the hibernation cycles of mammals. One effect of administering the thyronamines is a severe drop in body temperature.; Iodide is actively absorbed from the bloodstream and concentrated in the thyroid follicles. (If there is a deficiency of dietary iodine, the thyroid enlarges in an attempt to trap more iodine, resulting in goitre.) Via a reaction with the enzyme thyroperoxidase, iodine is covalently bound to tyrosine residues in the thyroglobulin molecules, forming monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and diiodotyrosine (DIT). Linking two moieties of DIT produces thyroxine. Combining one particle of MIT and one particle of DIT produces triiodothyronine.; Both T3 and T4 are used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism). They are both absorbed well by the gut, so can be given orally. Levothyroxine, the most commonly used synthetic thyroxine form, is a stereoisomer of physiological thyroxine, which is metabolized more slowly and hence usually only needs once-daily administration. Natural desiccated thyroid hormones, which are derived from pig thyroid glands, are a "natural" hypothyroid treatment containing 20% T3 and traces of T2, T1 and calcitonin.; this plays an important role in the hibernation cycles of mammals. One effect of administering the thyronamines is a severe drop in body temperature.; The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism.; The thyronamines function via some unknown mechanism to inhibit neuronal activity [HMDB] |
|---|
| CAS Number | 51-48-9 |
|---|
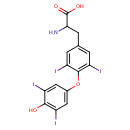
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (-)-Thyroxine | HMDB | | 3,3',5,5'-Tetraiodo-L-thyronine | ChEBI | | 3,3',5,5''-tetraiodo-L-thyronine | HMDB | | 3,5,3',5'-TETRAIODO-L-thyronine | ChEBI | | 3,5,3',5'-Tetraiodothyronine | HMDB | | 3,5,3'5'-Tetraiodo-L-thyronine | HMDB | | 4-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodo-L-phenylalanine | ChEBI | | D-Thyroxine | HMDB | | DL-Thyroxin | HMDB | | Henning | HMDB | | L-3,5,3',5'-Tetraiodothyronine | HMDB | | L-T4 | ChEBI | | L-Thyroxin | HMDB | | L-Thyroxine | ChEBI | | Laevothyroxinum | HMDB | | Levothroid | HMDB | | Levothyroxin | ChEBI | | Levothyroxine sodium | HMDB | | Levothyroxinum | HMDB | | Levoxyl | HMDB | | LT4 | ChEBI | | O-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenyl)-3,5-diiodo-L-tyrosine | ChEBI | | Prestwick_548 | HMDB | | S-Thyroxine | manual | | Synthroid | HMDB | | T4 | ChEBI | | Tetraiodothyronine | HMDB | | Tetramet | HMDB | | THX | HMDB | | Thyratabs | HMDB | | Thyrax | HMDB | | Thyreoideum | HMDB | | Thyroxin | HMDB | | Thyroxinal | HMDB | | Thyroxine I 125 | HMDB | | Thyroxine iodine | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C15H11I4NO4 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C15H11I4NO4/c16-8-4-7(5-9(17)13(8)21)24-14-10(18)1-6(2-11(14)19)3-12(20)15(22)23/h1-2,4-5,12,21H,3,20H2,(H,22,23) |
|---|
| InChI Key | XUIIKFGFIJCVMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | NC(CC1=CC(I)=C(OC2=CC(I)=C(O)C(I)=C2)C(I)=C1)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 776.87 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 776.686681525 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenylalanine and derivatives. Phenylalanine and derivatives are compounds containing phenylalanine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of phenylalanine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Phenylalanine and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Phenylalanine or derivatives
- Diphenylether
- Diaryl ether
- 3-phenylpropanoic-acid
- Alpha-amino acid
- Amphetamine or derivatives
- Phenoxy compound
- 2-iodophenol
- 2-halophenol
- Phenol ether
- Iodobenzene
- Halobenzene
- Aralkylamine
- Phenol
- Aryl halide
- Aryl iodide
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Benzenoid
- Amino acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Ether
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organohalogen compound
- Organoiodide
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 50 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | C539 |
|---|
| AKSci | J10324 |
|---|
| Carbosynth | HMDB0001918 |
|---|
| Cayman Chemical | 14116 |
|---|
| Glentham | GP9966 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0001918 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | T425600 |
|---|