| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:30:23 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:21 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000388 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB000461 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | L-Saccharopine |
|---|
| Description | Amino acid from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Neurospora crassaand is also found in mushrooms and seeds
Saccharopine is an intermediate in the degradation of lysine, formed by condensation of lysine and alpha-ketoglutarate. The saccharopine pathway is the main route for lysine degradation in mammal and its first two reactions are catalyzed by enzymatic activities known as lysine-oxoglutarate reductase (LOR) and saccharopine dehydrogenase (SDH), which reside on a single bifunctional polypeptide (EC EC 1.5.1.8, LOR/SDH). The reactions involved by saccharopine dehydrogenases have a very strict substrate specificity for L-lysine, 2-oxoglutarate and NADPH. LOR/SDH has been detected in a number of mammalian tissues, mainly in the liver and kidney, contributing not only to the general nitrogen balance in the organism but also to the controlled conversion of lysine into ketone bodies. A tetrameric form has also been observed in human liver and placenta. LOR activity has also been detected in brain mitochondria during embryonic development, and this opens the question of whether the degradation of lysine has any functional significance during brain development and puts a new focus on the nutritional requirements for lysine in gestation and infancy. Finally, LOR and/or SDH deficiencies seem to be involved in a human autosomic genetic disorder known as familial hyperlysinemia, which is characterized by serious defects in the functioning of the nervous system, and characterized by deficiency in lysine-ketoglutarate reductase, saccharopine dehydrogenase, and saccharopine oxidoreductase activities. Saccharopinuria (high amounts of saccharopine in the urine) and saccharopinemia (an excess of saccharopine in the blood) are conditions present in some inherited disorders of lysine degradation. (PMID: 463877, 10567240, 10772957, 4809305); Saccharopine is an intermediate in the metabolism of amino acid lysine. It is a precursor of lysine in the alpha-aminoadipate pathway which occurs in a few lower fungi, the higher fungi, and euglenids. In mammals and higher plants saccharopine is an intermediate in the degradation of lysine, formed by condensation of lysine and alpha-ketoglutarate. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 997-68-2 |
|---|
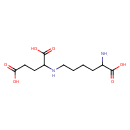
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (S)-N-(5-amino-5-carboxypentyl)-L-Glutamic acid | biospider | | Epsilon-N-(L-Glutar-2-yl)-L-lysine | biospider | | L-Glutamic acid, N-(5-amino-5-carboxypentyl)-, (S)- | biospider | | L-N-(5-amino-5-carboxypentyl)-Glutamic acid | biospider | | L-saccharopin | biospider | | L-saccharopine | biospider | | N-(5-amino-5-carboxypentyl)-glutamic acid | biospider | | N-(5-amino-5-carboxypentyl)-L-glutamic acid | biospider | | N-(5-AMINO-5-CARBOXYPENTYL)GLUTAMIC ACID | biospider | | N-[(5S)-5-amino-5-carboxypentyl]-L-Glutamic acid | biospider | | N-[(S)-5-amino-5-Carboxypentyl]-L-glutamate | Generator | | N-[(S)-5-Amino-5-carboxypentyl]-L-glutamic acid | biospider | | N(6)-(L-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine | biospider | | N6-(L-1,3-Dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine | biospider | | Saccharopin | biospider | | Saccharopine | biospider | | Saccharopine; L-form | db_source | | SHR | biospider |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C11H20N2O6 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 2-[(5-amino-5-carboxypentyl)amino]pentanedioic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C11H20N2O6/c12-7(10(16)17)3-1-2-6-13-8(11(18)19)4-5-9(14)15/h7-8,13H,1-6,12H2,(H,14,15)(H,16,17)(H,18,19) |
|---|
| InChI Key | ZDGJAHTZVHVLOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | NC(CCCCNC(CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 276.2863 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 276.132136382 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as glutamic acid and derivatives. Glutamic acid and derivatives are compounds containing glutamic acid or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of glutamic acid at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Glutamic acid and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Glutamic acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid
- Tricarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Amino fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Secondary aliphatic amine
- Secondary amine
- Amine
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 257-259° dec. | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 30 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | S808340 |
|---|