| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:30:23 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:21 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000387 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB000476 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | N6-Acetyl-L-lysine |
|---|
| Description | Isolated from sugarbeet (Beta vulgaris)
N-acetyl-lysine is an acetylated amino acid. Post-translational lysine-acetylation is one of two major modifications of lysine residues in various proteins. Acetylation of specific lysine residues in the N-terminal domains of core histones is a biochemical marker of active genes. Acetylation is now known to play a major role in eukaryotic transcription. Specifically, acetyltransferase enzymes that act on particular lysine side chains of histones and other proteins are intimately involved in transcriptional activation. By modifying chromatin proteins and transcription-related factors, these acetylases are believed to regulate the transcription of many genes. The best-characterized mechanism is acetylation, catalyzed by histone acetyltransferase (HAT) enzymes. HATs function enzymatically by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) to the -amino group of certain lysine side chains within a histone's basic N-terminal tail region. Within a histone octamer, these regions extend out from the associated globular domains, and in the context of a nucleosome, they are believed to bind the DNA through charge interactions (positively charged histone tails associated with negatively charged DNA) or mediate interactions between nucleosomes. Lysine acetylation, which neutralizes part of a tail region's positive charge, is postulated to weaken histone-DNA or nucleosome-nucleosome interactions and/or signal a conformational change, thereby destabilizing nucleosome structure or arrangement and giving other nuclear factors, such as the transcription complex, more access to a genetic locus. In agreement with this is the fact that acetylated chromatin has long been associated with states of transcriptional activation. Specific recognition of N-acetyl-lysine is a conserved function of all bromodomains found in different proteins, recognized as an emerging intracellular signaling mechanism that plays critical roles in regulating gene transcription, cell-cycle progression, apoptosis, DNA repair, and cytoskeletal organization. (PMID 9169194, 10827952, 17340003, 16247734, 9478947, 10839822). |
|---|
| CAS Number | 692-04-6 |
|---|
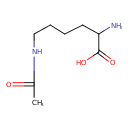
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (2S)-6-(acetylamino)-2-Aminohexanoate | Generator | | (2S)-6-(acetylamino)-2-aminohexanoic acid | biospider | | E-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | E-n-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | E-n-acetyllysine | biospider | | Epsilon-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | Epsilon-n-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | Epsilon-n-acetyllysine | biospider | | L-e-n-acetyllysine | biospider | | L-epsilon-n-acetyllysine | biospider | | N-e-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | N-e-acetyllysine | biospider | | N-epsilon-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | N-epsilon-acetyllysine | biospider | | N(6)-Acetyl-L-lysine | biospider | | N(6)-ACETYLLYSINE | biospider | | N(epsilon)-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | N(Z)-Acetyl-L-lysine | Generator | | N(Z)-Acetyllysine | Generator | | N(zeta)-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | N(zeta)-acetyllysine | biospider | | N(ζ)-acetyl-L-lysine | Generator | | N(ζ)-acetyllysine | Generator | | N6-Acetyl-L-lysine | biospider | | N6-Acetyllysine | biospider | | Ne-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | Ne-acetyllysine | biospider | | Nepsilon-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | Omega-n-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider | | W-n-acetyl-l-lysine | biospider |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H16N2O3 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 2-amino-6-acetamidohexanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H16N2O3/c1-6(11)10-5-3-2-4-7(9)8(12)13/h7H,2-5,9H2,1H3,(H,10,11)(H,12,13) |
|---|
| InChI Key | DTERQYGMUDWYAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CC(=O)NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 188.2242 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 188.116092388 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-amino acid
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Amino fatty acid
- Fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Acetamide
- Carboxamide group
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Amino acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | 250 | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 100 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | V7322 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | E588725 |
|---|