| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:29:30 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:18 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000257 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | L-Carnosine |
|---|
| Description | Occurs in meats
Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) is a dipeptide of the amino acids beta-alanine and histidine. It is highly concentrated in muscle and brain tissues.; Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) is found exclusively in animal tissues. It is a dipeptide of the amino acids beta-alanine and histidine. Carnosine has the potential to suppress many of the biochemical changes (e.g., protein oxidation, glycation, AGE formation, and cross-linking) that accompany aging and associated pathologies (PMID 16804013). It is highly concentrated in muscle and brain tissues. Some autistics patients take it as a dietary supplement, and attribute an improvement in their condition to it. Supplemental carnosine may increase corticosterone levels. This may explain the "hyperactivity" seen in autistic subjects at higher doses. Carnosine also exhibits some antioxidant effects. The antioxidant mechanism of carnosine is attributed to its chelating effect against metal ions, superoxide dismutase (SOD)-like activity, ROS and free radicals scavenging ability (PMID 16406688); Some studies have detected beneficial effects of N-acetyl-carnosine in preventing and treating cataracts of the eyes; in one of these, carnosine was found to reduce cloudiness in rat lenses that were exposed to guanidine to cause cataracts. However, claims that carnosine confers these and other posited ophthamological benefits are, as of yet, insufficiently supported for endorsement by the mainstream medical community; Britain's Royal College of Ophthamologists, for instance, has asserted that neither safety nor efficacy has been sufficiently demonstrated to recommend carnosine's use as a topical treatment for cataracts. Carnosine is a biomarker for the consumption of meat. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 305-84-0 |
|---|
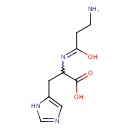
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| β-alanyl-l-histidine | biospider | | b-Alanyl-L-histidine | HMDB | | b-Alanylhistidine | HMDB | | Beta-alanyl-l-histidine | biospider | | beta-Alanylhistidine | HMDB | | Carnosine | ChEBI | | Carnosine; L-form | db_source | | Ignotine | HMDB | | Karnozin | HMDB | | Karnozzn | HMDB | | L-carnosine | biospider | | L-histidine, n-β-alanyl- | biospider | | N-(3-Aminopropanoyl)histidine | HMDB | | N-(b-Alanyl)-L-histidine | HMDB | | N-b-Alanyl-L-histidine | HMDB | | N-beta-Alanyl-L-histidine | HMDB | | Nalpha-(b-alanyl)-L-histidine | Generator | | Nalpha-(beta-alanyl)-L-histidine | ChEBI | | Nalpha-(β-alanyl)-L-histidine | Generator | | Sevitin | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC name | Not Available |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C9H14N4O3/c10-2-1-8(14)13-7(9(15)16)3-6-4-11-5-12-6/h4-5,7H,1-3,10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)(H,15,16) |
|---|
| InChI Key | CQOVPNPJLQNMDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | NCCC(=O)NC(CC1=CNC=N1)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 226.2325 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 226.106590334 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Classification | Not classified |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 246-250° dec. | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 2 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | F589 |
|---|
| AKSci | J30017 |
|---|
| AKSci | J91402 |
|---|
| Glentham | GE5095 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0000033 |
|---|
| Tokyo Chemical Industry | HMDB0000033 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | C184190 |
|---|