| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:29:13 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:16 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000210 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB000567 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | L-DOPA |
|---|
| Description | L-Dopa, also known as dopar or dopaston, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tyrosine and derivatives. Tyrosine and derivatives are compounds containing tyrosine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of tyrosine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. L-Dopa is a very strong basic compound (based on its pKa). L-Dopa exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. Within humans, L-dopa participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, L-dopa and tetrahydrobiopterin can be converted into dopamine and 4a-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin through its interaction with the enzyme aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase. In addition, L-dopa can be converted into dopaquinone; which is catalyzed by the enzyme tyrosinase. In humans, L-dopa is involved in the metabolic disorder called hawkinsinuria. L-Dopa is an odorless tasting compound. Outside of the human body, L-Dopa is found, on average, in the highest concentration within a few different foods, such as broad beans, swiss chards, and yellow wax beans and in a lower concentration in spinachs, garden onions, and green beans. L-Dopa has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as chicory roots, bitter gourds, mustard spinachs, pistachio, and savoy cabbages. This could make L-dopa a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. L-Dopa is a potentially toxic compound. L-Dopa, with regard to humans, has been found to be associated with several diseases such as eosinophilic esophagitis and alzheimer's disease; L-dopa has also been linked to several inborn metabolic disorders including aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency and sepiapterin reductase deficiency. An optically active form of dopa having L-configuration. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 59-92-7 |
|---|
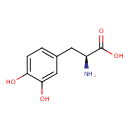
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (-)-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | biospider | | (-)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | biospider | | (-)-DOPA | biospider | | (2S)-2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate | biospider | | (2S)-2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid | biospider | | β-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | biospider | | β-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | biospider | | 2-Amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid; L-form | db_source | | 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | biospider | | 3-Hydroxy-L-tyrosine | biospider | | 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine | biospider | | 3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl-L-alanine | biospider | | Alanine, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-, (-)- | biospider | | Alanine, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-, L- | biospider | | b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-a-L-alanine | biospider | | b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | biospider | | b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | Generator | | Bendopa | db_source | | beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-L-alanine | HMDB | | beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | ChEBI | | beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | ChEBI | | Cidandopa | biospider | | Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine | biospider | | Dihydroxyphenylalanine | HMDB | | DOPA | biospider | | Dopaflex | biospider | | Dopaidan | biospider | | Dopal | biospider | | Dopalina | biospider | | Dopar | db_source | | Doparkine | biospider | | Doparl | biospider | | Dopasol | biospider | | Dopaston | biospider | | Dopastone | HMDB | | Dopastral | biospider | | Dopicar | biospider | | Doprin | biospider | | Eldopal | biospider | | Eldopar | biospider | | Eldopatec | biospider | | Eurodopa | biospider | | Helfo-dopa | biospider | | Insulamina | biospider | | L-(-)-DOPA | biospider | | L-(3, 4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | biospider | | L-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-α-alanine | biospider | | L-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | biospider | | L-β-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | biospider | | L-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-Alanine | biospider | | L-3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | biospider | | L-3-Hydroxytyrosine | biospider | | L-4-5-Dihydroxyphenylalanine | biospider | | L-b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-a-alanine | HMDB | | L-b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | Generator | | L-beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-alanine | HMDB | | L-beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | ChEBI | | L-dihydroxyphenylalanine | biospider | | L-DOPA | biospider | | L-Tyrosine, 3-hydroxy- | biospider | | L-β-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | Generator | | Laradopa | biospider | | Larodopa | db_source | | Ledopa | biospider | | Levedopa | HMDB | | Levodopa | ChEBI | | Levodopa, BAN, INN, JAN, USAN | db_source | | Levodopum | ChEBI | | Levopa | db_source | | Maipedopa | biospider | | Parda | biospider | | Pardopa | biospider | | Prodopa | HMDB | | Syndopa | biospider | | Veldopa | db_source | | Weldopa | biospider | | β-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | Generator | | β-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | Generator |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C9H11NO4 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | (2S)-2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C9H11NO4/c10-6(9(13)14)3-5-1-2-7(11)8(12)4-5/h1-2,4,6,11-12H,3,10H2,(H,13,14)/t6-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | WTDRDQBEARUVNC-LURJTMIESA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | N[C@@H](CC1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 197.1879 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 197.068807845 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tyrosine and derivatives. Tyrosine and derivatives are compounds containing tyrosine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of tyrosine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Tyrosine and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Tyrosine or derivatives
- Phenylalanine or derivatives
- 3-phenylpropanoic-acid
- Alpha-amino acid
- Amphetamine or derivatives
- L-alpha-amino acid
- Catechol
- 1-hydroxy-4-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Aralkylamine
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Phenol
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Benzenoid
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary amine
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | -2.39 | SANGSTER (1993) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 5 mg/mL at 20 oC | YALKOWSKY,SH & DANNENFELSER,RM (1992) |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 285.5° dec. | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 2 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | H813 |
|---|
| AKSci | J10404 |
|---|
| AKSci | J90768 |
|---|
| Cayman Chemical | 13248 |
|---|
| Cayman Chemical | HMDB0000181 |
|---|
| Glentham | GM9724 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0000181 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | D533751 |
|---|