| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:28:09 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:12 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000088 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB012160 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Riboflavine |
|---|
| Description | Riboflavin, also known as lactoflavin or vitamin B2, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as flavins. Flavins are compounds containing a flavin (7,8-dimethyl-benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione) moiety, with a structure characterized by an isoalloaxzine tricyclic ring. It occurs in the free form only in the retina of the eye, in whey, and in urine; its principal forms in tissues and cells are as flavin mononucleotide and flavin-adenine dinucleotide. Riboflavin is a drug which is used for the treatment of ariboflavinosis (vitamin b2 deficiency). The antioxidant activity of riboflavin is principally derived from its role as a precursor of FAD and the role of this cofactor in the production of the antioxidant reduced glutathione. Riboflavin is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Riboflavin exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. Binds to riboflavin hydrogenase, riboflavin kinase, and riboflavin synthase. In humans, riboflavin is involved in the metabolic disorder called the medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (mcad) pathway. Outside of the human body, Riboflavin is found, on average, in the highest concentration within a few different foods, such as saffrons, saskatoon berries, and leavening agents and in a lower concentration in grape wines, hippoglossus (common halibut), and spiny lobsters. Riboflavin has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as bog bilberries, lowbush blueberries, greenthread tea, nanking cherries, and black radish. This could make riboflavin a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Riboflavin is a potentially toxic compound. Nutritional factor found in milk, eggs, malted barley, liver, kidney, heart, and leafy vegetables. The richest natural source is yeast. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 83-88-5 |
|---|
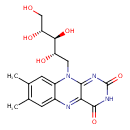
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (-)-Riboflavin | biospider | | 1-Deoxy-1-(3,4-dihydro-7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxobenzo[g]pteridin-10(2H)-yl)-D-ribitol | HMDB | | 1-Deoxy-1-(3,4-dihydro-7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxobenzo[g]pteridin-10(2H)-yl)-D-ribitol, 9CI | db_source | | 1-Deoxy-1-(7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydrobenzo[g]pteridin-10(2H)-yl)pentitol | ChEBI | | 6,7-Dimethyl-9-D-ribitylisoalloxazine | biospider | | 6,7-Dimethyl-9-ribitylisoalloxazine | HMDB | | 7,8-Dimethyl-10-(D-ribo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)-benzo[g]pteridine-2,4(3H,10H)-dione | HMDB | | 7,8-Dimethyl-10-(D-ribo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)benzo[g]pteridine-2,4(3H,10H)-dione | ChEBI | | 7,8-Dimethyl-10-(D-ribo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)isoalloxazine | ChEBI | | 7,8-Dimethyl-10-ribitylisoalloxazine | biospider | | Beflavin | HMDB | | Beflavine | biospider | | Benzo[g]pteridine riboflavin deriv. | HMDB | | e 101 | HMDB | | E101 | db_source | | Flavaxin | db_source | | Flavin BB | biospider | | Flaxain | biospider | | Food Yellow 15 | biospider | | Hyre | HMDB | | Isoalloxazine, 7,8-dimethyl-10-D-ribityl- | biospider | | Lactobene | biospider | | Lactoflavin | biospider | | Lactoflavine | db_source | | Ovoflavine | db_source | | Ribipca | biospider | | Ribocrisina | biospider | | Riboderm | biospider | | Riboflavin | biospider | | Riboflavina | ChEBI | | Riboflavinum | ChEBI | | Ribosyn | biospider | | Ribotone | biospider | | Ribovel | biospider | | Russupteridine yellow III | db_source | | San yellow b | HMDB | | Vitaflavine | biospider | | Vitamin B2 | db_source | | Vitamin G | db_source | | Vitasan b2 | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C17H20N4O6 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 7,8-dimethyl-10-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl]-2H,3H,4H,10H-benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C17H20N4O6/c1-7-3-9-10(4-8(7)2)21(5-11(23)14(25)12(24)6-22)15-13(18-9)16(26)20-17(27)19-15/h3-4,11-12,14,22-25H,5-6H2,1-2H3,(H,20,26,27)/t11-,12+,14-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | AUNGANRZJHBGPY-SCRDCRAPSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CC1=C(C)C=C2N(C[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)C3=NC(=O)NC(=O)C3=NC2=C1 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 376.3639 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 376.138284392 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as flavins. Flavins are compounds containing a flavin (7,8-dimethyl-benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione) moiety, with a structure characterized by an isoalloaxzine tricyclic ring. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Pteridines and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Alloxazines and isoalloxazines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Flavins |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Flavin
- Diazanaphthalene
- Quinoxaline
- Pyrimidone
- Pyrazine
- Pyrimidine
- Benzenoid
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Vinylogous amide
- Secondary alcohol
- Lactam
- Polyol
- Azacycle
- Alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | -1.46 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 0.0847 mg/mL at 25 oC | YALKOWSKY,SH & DANNENFELSER,RM (1992) |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 280° dec. | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 2 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | J10875 |
|---|
| AKSci | J40034 |
|---|
| AKSci | J92627 |
|---|
| AKSci | R437 |
|---|
| Glentham | GP0758 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0000244 |
|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | HMDB0000244 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | R414995 |
|---|