| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:28:03 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:12 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000081 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB000570 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | L-Proline |
|---|
| Description | Proline or L-proline abbreviated Pro or is one of the twenty amino acids used in living organisms as the building blocks of proteins. Proline is sometimes called an imino acid, although the IUPAC definition of an imine requires a carbon-nitrogen double bond. Proline is a non-essential amino acid that is largely synthesized from glutamic acid. While proline biosynthetic pathways exist from eubacteria to eukaryotes, in the most prevalent pathway, proline is cyclized from glutamate. First glutamate is phosphorylated to gamma-glutamyl phosphate by gamma-glutamyl kinase, then second, reduced to gamma-glutamyl semialdehyde by gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase, then third, cyclized spontaneously to delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate and fourth, reduced to proline by delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase. In higher plants and animals, the first two steps are catalysed by a bi-functional delta(1) -pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase. Alternative pathways of proline formation use the initial steps of the arginine biosynthetic pathway to ornithine, which can be converted to delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate by ornithine aminotransferase and then reduced to proline or converted directly to proline by ornithine cyclodeaminase (PMID: 25367752). Proline is an essential component of collagen and is important for proper functioning of joints and tendons. It is a potential endogenous excitotoxin/neurotoxin, which causes damage to nerve cells and nerve tissues. Proline, when injected into the brains of rats, non-selectively destroyed pyramidal and granule cells (PMID: 3409032) suggesting that it can act as a neurotoxin. Proline can also be a metabotoxin which is an endogenously produced metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels. At least five inborn errors of metabolism, including hyperprolinemia type I, hyperprolinemia type II, iminoglycinuria, prolinemia type II, and pyruvate carboxylase deficiency are associated with chronically high levels of proline (PMID: 18806117). Hyperprolinemia I and II are caused by deficiencies in the enzymatic activities of proline dehydrogenase and Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase, respectively. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 147-85-3 |
|---|
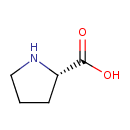
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (-)-(S)-Proline | biospider | | (-)-2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylate | biospider | | (-)-2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | biospider | | (-)-Proline | biospider | | (2S)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate | Generator | | (2S)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | biospider | | (L)-Proline | biospider | | (S)-(-)-Proline | biospider | | (S)-(-)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate | biospider | | (S)-(-)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | biospider | | (S)-2-Carboxypyrrolidine | biospider | | (S)-2-Pyrralidinecarboxylate | biospider | | (S)-2-Pyrralidinecarboxylic acid | biospider | | (S)-2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylate | biospider | | (S)-2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | biospider | | (S)-Proline | biospider | | (S)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate | Generator | | (S)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | biospider | | 2-Pyrralidinecarboxylic acid, (S)- | biospider | | 2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylate | Generator | | 2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | ChEBI | | 2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid, (S)- | biospider | | FEMA 3319 | db_source | | L-(-)-Proline | biospider | | L-a-Pyrrolidinecarboxylate | Generator | | L-a-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | Generator | | L-alpha-Pyrrolidinecarboxylate | Generator | | L-alpha-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | biospider | | L-Prolin | ChEBI | | L-Proline | biospider | | L-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate | Generator | | L-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | ChEBI | | L-α-pyrrolidinecarboxylate | Generator | | L-α-pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | Generator | | P | ChEBI | | Prolina | ChEBI | | PROLINE | ChEBI | | Proline, 9CI; L-form | db_source | | Prolinum | ChEBI |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC name | Not Available |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C5H9NO2/c7-5(8)4-2-1-3-6-4/h4,6H,1-3H2,(H,7,8)/t4-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | ONIBWKKTOPOVIA-BYPYZUCNSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | OC(=O)[C@@H]1CCCN1 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 115.1305 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 115.063328537 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as proline and derivatives. Proline and derivatives are compounds containing proline or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of proline at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Proline and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Proline or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid
- L-alpha-amino acid
- Pyrrolidine carboxylic acid
- Pyrrolidine carboxylic acid or derivatives
- Pyrrolidine
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Secondary aliphatic amine
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Secondary amine
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Azacycle
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | -2.54 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 162 mg/mL at 25 oC | MERCK INDEX (1996) |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 220-222° dec. | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 1 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | A131 |
|---|
| AKSci | J90475 |
|---|
| Glentham | GM1129 |
|---|
| Glentham | GM9897 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0000162 |
|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | HMDB0000162 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | P755995 |
|---|