| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:28:02 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:12 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000079 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB022123 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | DL-Homocystine |
|---|
| Description | Homocystine is the double-bonded form of homocysteine, but it occurs only transiently before being converted to the harmless cystathionine via a vitamin B6-dependent enzyme.
Homocystine and homocysteine-cysteine mixed disulfide account for >98% of total homocysteine in plasma from healthy individuals. (PMID 11592966)
Oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is thought to be a major factor in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. Elevated plasma homocysteine is an accepted risk factor for atherosclerosis, and may act through LDL oxidation, although this is controversial. However, the major thiol in plasma is cysteine, which is present at concentrations approximately 10 times greater than homocysteine; therefore homocystine in plasma is insignificant, and consequently homocystine is unlikely to influence LDL oxidation in vivo. (PMID 14732479)
Increasing evidence supports a role for an elevation of homocysteine in schizophrenia. It has been demonstrated that neural tube defects are related to a genetic defect in homocysteine metabolism. Sufficient intake of folic acid is believed to reduce this risk by enhancing methylation of homocysteine and its conversion to methionine, thereby compensating for this genetic defect. Plasma homocysteine levels are elevated when folate levels are in the lower half of the normal range. (PMID 16143442 ) [HMDB] |
|---|
| CAS Number | 870-93-9 |
|---|
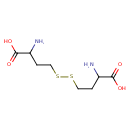
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| 4,4'-Dithiobis | hmdb | | 4,4'-Dithiobis(2-aminobutyrate) | Generator | | DL-Homocystine | hmdb | | Homocystine | hmdb |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H16N2O4S2 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 2-amino-4-[(3-amino-3-carboxypropyl)disulfanyl]butanoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H16N2O4S2/c9-5(7(11)12)1-3-15-16-4-2-6(10)8(13)14/h5-6H,1-4,9-10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14) |
|---|
| InChI Key | ZTVZLYBCZNMWCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | NC(CCSSCCC(N)C(O)=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 268.354 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 268.05514839 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-amino acid
- Thia fatty acid
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Organic disulfide
- Amino acid
- Dialkyldisulfide
- Sulfenyl compound
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Primary amine
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 2 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | C418 |
|---|