| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:27:36 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:10 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000036 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB012266 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Adenine |
|---|
| Description | Widespread throughout animal and plant tissue, purine components of DNA, RNA, and coenzymes. Vitamin
Adenine (sometimes known as vitamin B4) combines with the sugar ribose to form adenosine, which in turn can be bonded with from one to three phosphoric acid units, yielding AMP, ADP and ATP . These adenine derivatives perform important functions in cellular metabolism. Adenine is one of four nitrogenous bases utilized in the synthesis of nucleic acids. A modified form of adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP) is an imporant secondary messenger in the propagation of many hormonal stimuli. Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes. Adenosine (adenine with a ribose group) causes transient heart block in the AV node of the heart. In individuals suspected of suffering from a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify the rhythm. Certain SVTs can be successfully terminated with adenosine.; Adenine forms adenosine, a nucleoside, when attached to ribose, and deoxyadenosine when attached to deoxyribose. It forms adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a nucleotide, when three phosphate groups are added to adenosine. Adenosine triphosphate is used in cellular metabolism as one of the basic methods of transferring chemical energy between chemical reactions.; Adenine is a nucleobase (a purine derivative) with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. The shape of adenine is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.; Adenine is a purine base. Adenine is found in both DNA and RNA. Adenine is a fundamental component of adenine nucleotides. Adenine forms adenosine, a nucleoside, when attached to ribose, and deoxyadenosine when attached to deoxyribose; Adenine is one of the two purine nucleobases (the other being guanine) used in forming nucleotides of the nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine binds to thymine via two hydrogen bonds to assist in stabilizing the nucleic acid structures. In RNA, which is used in the cytoplasm for protein synthesis, adenine binds to uracil.; In older literature, adenine was sometimes called Vitamin B4. It is no longer considered a true vitamin or part of the Vitamin B complex. However, two B vitamins, niacin and riboflavin, bind with adenine to form the essential cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), respectively. Hermann Emil Fischer was one of the early scientists to study Adenine.; it forms adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a nucleotide, when three phosphate groups are added to adenosine. Adenosine triphosphate is used in cellular metabolism as one of the basic methods of transferring chemical energy between chemical reactions.; Purine inborn errors of metabolism (IEM) are serious hereditary disorders, which should be suspected in any case of neonatal fitting, failure to thrive, recurrent infections, neurological deficit, renal disease, self-mutilation and other manifestations. Investigation usually starts with uric acid (UA) determination in urine and plasma. (OMIM 300322, 229600, 603027, 232400, 232600, 232800, 201450, 220150, 232200, 162000, 164050, 278300). (PMID: 17052198, 17520339). |
|---|
| CAS Number | 73-24-5 |
|---|
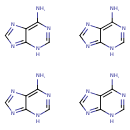
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| 1,6-Dihydro-6-iminopurine | biospider | | 1h-purin-6-amine | biospider | | 1H-Purin-6-amine (9CI) | biospider | | 1H-Purin-6-amine, 9CI | db_source | | 1H-Purine-6-amine | biospider | | 1H-Purine, 6-amino | biospider | | 1H-Purine, 6-amino- | biospider | | 2-aminopurine | biospider | | 2'-DEOXY-ADENOSINE-3'-5'-DIPHOSPHATE | biospider | | 3, 6-Dihydro-6-iminopurine | biospider | | 3,6-Dihydro-6-iminopurine | biospider | | 4, Vitamin B | biospider | | 6-Amino-1H-purine | biospider | | 6-Amino-3H-purine | biospider | | 6-Amino-7H-purine | biospider | | 6-Amino-9H-purine | biospider | | 6-amino-Purine | biospider | | 6-Aminopurine | db_source | | 7H-Purin-6-amine | biospider | | 9H-Purin-6-amine | biospider | | 9H-Purin-6-yl-amin | biospider | | 9H-purin-6-ylamine | biospider | | 9H-Purine-6-amine | biospider | | 9H-Purine, 1, 6-dihydro-6-imino- | biospider | | 9H-Purine, 1,6-dihydro-6-imino- | biospider | | A, ade, adeninimine | biospider | | ABG | biospider | | ADE | biospider | | Adenin | biospider | | Adenine (8CI) | biospider | | Adenine (jan/usp) | biospider | | Adenine (van ) | biospider | | Adenine (van) | biospider | | Adenine [jan] | biospider | | Adenine-8-14C | biospider | | Adenine-ring | biospider | | Adeninimine | biospider | | ANE | biospider | | ANP | biospider | | B 4, Vitamin | biospider | | Leuco-4 | biospider | | Leucon | biospider | | Leucon (TN) | biospider | | Pedatisectine b | biospider | | Purine, 6-amino- | biospider | | Vitamin B 4 | biospider | | Vitamin B4 | db_source |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H20N20 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | tetrakis(3H-purin-6-amine) |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/4C5H5N5/c4*6-4-3-5(9-1-7-3)10-2-8-4/h4*1-2H,(H3,6,7,8,9,10) |
|---|
| InChI Key | ZSIFYVSPMACPJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | NC1=C2N=CN=C2N=CN1.NC1=NC=NC2=C1NC=N2.NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2.NC1=C2N=CN=C2NC=N1 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 540.5068 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 540.21798074 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 6-aminopurines. These are purines that carry an amino group at position 6. Purine is a bicyclic aromatic compound made up of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Imidazopyrimidines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Purines and purine derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 6-aminopurines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 6-aminopurine
- Aminopyrimidine
- Imidolactam
- Pyrimidine
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Imidazole
- Azole
- Azacycle
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Not Available |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | -0.09 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 1.03 mg/mL at 25 oC | YALKOWSKY,SH & DANNENFELSER,RM (1992) |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 360-365 (anhyd.)° dec. | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 500 mg |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | D124 |
|---|
| AKSci | J20020 |
|---|
| AKSci | J70183 |
|---|
| AKSci | J90580 |
|---|
| AKSci | HMDB0000034 |
|---|
| Glentham | GE7863 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0000034 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | A280480 |
|---|