| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:27:27 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:10 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000024 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | L-Valine |
|---|
| Description | Widely distributed in nature as one of the principal protein amino acids. Dietary supplement
Branched chain amino acids (BCAA) are essential amino acids whose carbon structure is marked by a branch point. These three amino acids are critical to human life and are particularly involved in stress, energy and muscle metabolism. BCAA supplementation as therapy, both oral and intravenous, in human health and disease holds great promise. "BCAA" denotes valine, isoleucine and leucine which are branched chain essential amino acids. Despite their structural similarities, the branched amino acids have different metabolic routes, with valine going solely to carbohydrates, leucine solely to fats and isoleucine to both. The different metabolism accounts for different requirements for these essential amino acids in humans: 12 mg/kg, 14 mg/kg and 16 mg/kg of valine, leucine and isoleucine respectively. Furthermore, these amino acids have different deficiency symptoms. Valine deficiency is marked by neurological defects in the brain, while isoleucine deficiency is marked by muscle tremors.; Many types of inborn errors of BCAA metabolism exist, and are marked by various abnormalities. The most common form is the maple syrup urine disease, marked by a characteristic urinary odor. Other abnormalities are associated with a wide range of symptoms, such as mental retardation, ataxia, hypoglycemia, spinal muscle atrophy, rash, vomiting and excessive muscle movement. Most forms of BCAA metabolism errors are corrected by dietary restriction of BCAA and at least one form is correctable by supplementation with 10 mg of biotin daily. BCAA are decreased in patients with liver disease, such as hepatitis, hepatic coma, cirrhosis, extrahepatic biliary atresia or portacaval shunt; L-valine is a branched-chain essential amino acid (BCAA) that has stimulant activity. It promotes muscle growth and tissue repair. It is a precursor in the penicillin biosynthetic pathway. Valine is one of three branched-chain amino acids (the others are leucine and isoleucine) that enhance energy, increase endurance, and aid in muscle tissue recovery and repair. This group also lowers elevated blood sugar levels and increases growth hormone production. Supplemental valine should always be combined with isoleucine and leucine at a respective milligram ratio of 2:1:2. It is an essential amino acid found in proteins; Valine (abbreviated as Val or V) is an ?-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)2. L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. Along with leucine and isoleucine, valine is a branched-chain amino acid. It is named after the plant valerian. In sickle-cell disease, valine substitutes for the hydrophilic amino acid glutamic acid in hemoglobin. Because valine is hydrophobic, the hemoglobin does not fold correctly.; Valine is an essential amino acid, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. And will flow bood engorged pumps to the penile region. It is synthesized in plants via several steps starting from pyruvic acid. The initial part of the pathway also leads to leucine. The intermediate ?-ketovalerate undergoes reductive amination with glutamate. Enzymes involved in this biosynthesis include:; aromatic amino acids (AAA)-tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine, as well as methionine-are increased in these conditions. Valine in particular, has been established as a useful supplemental therapy to the ailing liver. All the BCAA probably compete with AAA for absorption into the brain. Supplemental BCAA with vitamin B6 and zinc help normalize the BCAA:AAA ratio. (http://www.dcnutrition.com). |
|---|
| CAS Number | 72-18-4 |
|---|
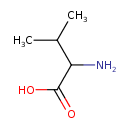
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (2S)-2-amino-3-Methylbutanoate | Generator | | (2S)-2-amino-3-Methylbutanoic acid | ChEBI | | (S)-2-amino-3-Methyl-butanoate | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-3-Methyl-butanoic acid | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-3-Methylbutanoate | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-3-Methylbutanoic acid | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-3-Methylbutyrate | HMDB | | (S)-2-amino-3-Methylbutyric acid | HMDB | | (S)-a-amino-b-Methylbutyrate | HMDB | | (S)-a-amino-b-Methylbutyric acid | HMDB | | (S)-alpha-amino-beta-Methylbutyrate | HMDB | | (S)-alpha-amino-beta-Methylbutyric acid | HMDB | | (S)-Valine | ChEBI | | 2-amino-3-Methylbutanoate | HMDB | | 2-amino-3-Methylbutanoic acid | HMDB | | 2-amino-3-Methylbutyrate | Generator | | 2-amino-3-Methylbutyric acid | ChEBI | | L-(+)-α-aminoisovaleric acid | biospider | | L-(+)-a-Aminoisovalerate | Generator | | L-(+)-a-Aminoisovaleric acid | Generator | | L-(+)-alpha-Aminoisovalerate | Generator | | L-(+)-alpha-Aminoisovaleric acid | ChEBI | | L-(+)-α-aminoisovalerate | Generator | | L-(+)-α-aminoisovaleric acid | Generator | | L-a-amino-b-Methylbutyrate | Generator | | L-a-amino-b-Methylbutyric acid | Generator | | L-alpha-amino-beta-Methylbutyrate | Generator | | L-alpha-amino-beta-Methylbutyric acid | ChEBI | | L-iso-C3H7CH(NH2)COOH | biospider | | L-Valin | ChEBI | | L-α-amino-β-methylbutyrate | Generator | | L-α-amino-β-methylbutyric acid | Generator | | V | ChEBI | | Val | ChEBI | | VALINE | ChEBI | | Valine; L-form | db_source |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC name | Not Available |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C5H11NO2/c1-3(2)4(6)5(7)8/h3-4H,6H2,1-2H3,(H,7,8) |
|---|
| InChI Key | KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CC(C)C(N)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 117.1463 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 117.078978601 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as valine and derivatives. Valine and derivatives are compounds containing valine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of valine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Valine and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Valine or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid
- Branched fatty acid
- Methyl-branched fatty acid
- Fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organopnictogen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Amine
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | -2.26 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 58.5 mg/mL at 25 oC | YALKOWSKY,SH & DANNENFELSER,RM (1992) |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 315 dec. (sealed tube) | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 1 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | G139 |
|---|
| AKSci | J92340 |
|---|
| Glentham | GM6473 |
|---|
| Glentham | GM3894 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0000883 |
|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | HMDB0000883 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | V094205 |
|---|