| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:27:19 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:10 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000016 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB003191 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | Taurine |
|---|
| Description | Essential nutrient obtained from diet and by in vivo synthysis from methionine and cysteine. Present in meats, fish, legumes, human milk, molluscs and other foods. Dietary supplement, e.g. in Red Bull drink. Taurine is a sulfur amino acid like methionine, cystine, cysteine and homocysteine. It is a lesser-known amino acid because it is not incorporated into the structural building blocks of protein. Yet taurine is an essential amino acid in pre-term and newborn infants of humans and many other species. Adults can synthesize their own taurine, yet are probably dependent in part on dietary taurine. Taurine is abundant in the brain, heart, breast, gallbladder and kidney and has important roles in health and disease in these organs. Taurine has many diverse biological functions serving as a neurotransmitter in the brain, a stabilizer of cell membranes and a facilitator in the transport of ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium. Taurine is highly concentrated in animal and fish protein, which are good sources of dietary taurine. It can be synthesized by the body from cysteine when vitamin B6 is present. Deficiency of taurine occurs in premature infants and neonates fed formula milk, and in various disease states. Inborn errors of taurine metabolism have been described. OMIM 168605, an unusual neuropsychiatric disorder inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion through 3 generations of a family. Symptoms began late in the fifth decade in 6 affected persons and death occurred after 4 to 6 years. The earliest and most prominent symptom was mental depression not responsive to antidepressant drugs or electroconvulsive therapy. Sleep disturbances, exhaustion and marked weight loss were features. Parkinsonism developed later, and respiratory failure occurred terminally. OMIM 145350 describes congestive cardiomyopathy and markedly elevated urinary taurine levels (about 5 times normal). Other family members had late or holosystolic mitral valve prolapse and elevated urinary taurine values (about 2.5 times normal). In 2 with mitral valve prolapse, congestive cardiomyopathy eventually developed while the amounts of urinary taurine doubled. Taurine, after GABA, is the second most important inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Its inhibitory effect is one source of taurine's anticonvulsant and antianxiety properties. It also lowers glutamic acid in the brain, and preliminary clinical trials suggest taurine may be useful in some forms of epilepsy. Taurine in the brain is usually associated with zinc or manganese. The amino acids alanine and glutamic acid, as well as pantothenic acid, inhibit taurine metabolism while vitamins A and B6, zinc and manganese help build taurine. Cysteine and B6 are the nutrients most directly involved in taurine synthesis. Taurine levels have been found to decrease significantly in many depressed patients. One reason that the findings are not entirely clear is because taurine is often elevated in the blood of epileptics who need it. It is often difficult to distinguish compensatory changes in human biochemistry from true metabolic or deficiency disease. Low levels of taurine are found in retinitis pigmentosa. Taurine deficiency in experimental animals produces degeneration of light-sensitive cells. Therapeutic applications of taurine to eye disease are likely to be forthcoming. Taurine has many important metabolic roles. Supplements can stimulate prolactin and insulin release. The parathyroid gland makes a peptide hormone called glutataurine (glutamic acid-taurine), which further demonstrates taurine's role in endocrinology. Taurine increases bilirubin and cholesterol excretion in bile, critical to normal gallbladder function. It seems to inhibit the effect of morphine and potentiates the effects of opiate antagonists. Low plasma taurine levels have been found in a variety of conditions, i.e., depression, hypertension, hypothyroidism, gout, institutionalized patients, infertility, obesity, kidney failure and others. (http://www.dcnutrition.com/AminoAcids/); Taurine is an essential dietary requirement for feline health, since cats cannot synthesize the compound. The absence of taurine causes a cat's retina to slowly degenerate, causing eye problems and (eventually) irreversible blindness ? a condition known as central retinal degeneration (CRD), as well as hair loss and tooth decay. It was discovered in 1987 that taurine deficiency can also cause feline dilated cardiomyopathy. Unlike CRD, the condition is reversible with supplementation. Taurine is now a requirement of the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) and any dry or wet food product labeled approved by the AAFCO should have a minimum of 0.1% taurine in dry food and 0.2% in wet food.; Taurine, or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic acid. It is also a major constituent of bile and can be found in the lower intestine and in small amounts in the tissues of many animals, including humans. Taurine is a derivative of the sulfur-containing (sulfhydryl) amino acid, cysteine. Taurine is one of the few known naturally occurring sulfonic acids. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 107-35-7 |
|---|
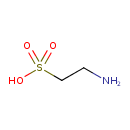
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| β-aminoethylsulfonic acid | biospider | | 1-Aminoethane-2-sulfonate | biospider | | 1-Aminoethane-2-sulfonic acid | biospider | | 2-Aminoethanesulfonate | biospider | | 2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid | ChEBI | | 2-Aminoethanesulphonate | Generator | | 2-Aminoethanesulphonic acid | Generator | | 2-aminoethyl sulfonate | biospider | | 2-Aminoethyl sulfonic acid | Generator | | 2-Aminoethyl sulphonate | Generator | | 2-Aminoethyl sulphonic acid | Generator | | 2-Aminoethylsulfonate | biospider | | 2-Aminoethylsulfonic acid | biospider | | 2-Sulfoethylamine | biospider | | Aminoethanesulfonic acid | biospider | | Aminoethylsulfonate | biospider | | Aminoethylsulfonic acid | db_source | | Aminoethylsulfonic acid (jan) | biospider | | Aminoethylsulphonate | Generator | | Aminoethylsulphonic acid | Generator | | Aminoetylsulphonic acid | biospider | | B-aminoethylsulfonate | biospider | | B-aminoethylsulfonic acid | biospider | | b-Aminoethylsulphonate | Generator | | b-Aminoethylsulphonic acid | Generator | | Beta-aminoethylsulfonate | biospider | | Beta-aminoethylsulfonic acid | biospider | | beta-Aminoethylsulphonate | Generator | | beta-Aminoethylsulphonic acid | Generator | | Ethanesulfonic acid, 2-amino- | biospider | | Ethanesulfonic acid, 2-amino- (9CI) | biospider | | Ethylaminesulfonic acid | db_source | | Ethylaminesulphonic acid | biospider | | FEMA 3813 | db_source | | L-taurine | biospider | | O-due | biospider | | TAU | biospider | | Taufon | biospider | | Taukard | biospider | | Tauphon | biospider | | Taurine | biospider | | Taurine (8CI) | biospider | | Taurine (JP15/USP/INN) | biospider | | Taurine (TN) | biospider | | Taurine [inn] | biospider | | Taurine, 8CI, INN | db_source | | β-aminoethylsulfonate | Generator | | β-aminoethylsulfonic acid | Generator | | β-aminoethylsulphonate | Generator | | β-aminoethylsulphonic acid | Generator |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C2H7NO3S |
|---|
| IUPAC name | 2-aminoethane-1-sulfonic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C2H7NO3S/c3-1-2-7(4,5)6/h1-3H2,(H,4,5,6) |
|---|
| InChI Key | XOAAWQZATWQOTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | NCCS(O)(=O)=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 125.147 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 125.014663785 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as organosulfonic acids. Organosulfonic acids are compounds containing the sulfonic acid group, which has the general structure RS(=O)2OH (R is not a hydrogen atom). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Organic sulfonic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Organosulfonic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Organosulfonic acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alkanesulfonic acid
- Sulfonyl
- Organosulfonic acid
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Organosulfur compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Amine
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | Not Available | |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 80.7 mg/mL at 20 oC | YALKOWSKY,SH & DANNENFELSER,RM (1992) |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 328° (320-325° dec.) | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 6 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| AKSci | I815 |
|---|
| AKSci | J90118 |
|---|
| Glentham | GP1188 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0000251 |
|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | HMDB0000251 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | T007850 |
|---|