| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:27:19 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:10 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000015 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB012802 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
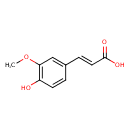
| Name | trans-Ferulic acid |
|---|
| Description | Ferulic acid, also known as (e)-ferulate or trans-ferulate, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxycinnamic acids. Hydroxycinnamic acids are compounds containing a cinnamic acid where the benzene ring is hydroxylated. Ferulic acid is a moderately weak acid (based on its pKa). Ferulic acid is a highly abundant phenolic phytochemical which is present in plant cell walls. In humans it can be readily absorbed by the small intestine and excreted through the urine. It is one of the most abundant phenolic acids in plants, varying from 5 g/kg in wheat bran to 9 g/kg in sugar-beet pulp and 50 g/kg in corn kernels. It occurs primarily in seeds and leaves both in its free form (albeit rarely) and covalently linked to lignin and other biopolymers. It is usually found as ester cross-links with polysaccharides in the cell wall, such as arabinoxylans in grasses, pectin in spinach and sugar beet, and xyloglucans in bamboo. It also can cross-link with a variety of plant proteins. Due to its phenolic nucleus and an extended side chain conjugation (carbohydrates and proteins), ferulic acid readily forms a resonance-stabilized phenoxy radical which accounts for its potent antioxidant potential. Food supplementation with curcumin and ferulic acid is considered a nutritional approach to reducing oxidative damage and amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease (PMID: 17127365, 1398220, 15453708, 9878519). Ferulic acid can be produced by a number of microbes including Pseudomonas and Saccharomyces (PMID: 8395165). It possesses antioxidant, anti-aging and anti-inflammatory properties. It protects the skin from damage by UV light and is used in skin care, sun care, hair care and color cosmetics. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 537-98-4 |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| (2E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoate | biospider | | (2E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid | biospider | | (2E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid | biospider | | (E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoate | biospider | | (E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid | biospider | | (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-cinnamate | biospider | | (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-cinnamic acid | biospider | | (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamate | biospider | | (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid | biospider | | (e)-4'-Hydroxy-3'-methoxycinnamate | Generator | | (E)-4'-Hydroxy-3'-methoxycinnamic acid | biospider | | (E)-Ferulate | biospider | | (E)-Ferulic acid | biospider | | 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-, (E)- | biospider | | 3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propenoate | Generator | | 3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propenoic acid | ChEBI | | 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxy-trans-cinnamate | Generator | | 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxy-trans-cinnamic acid | ChEBI | | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-(E)-cinnamic acid | biospider | | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamate | Generator | | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid | ChEBI | | Ferulate | Generator | | trans-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamate | biospider | | trans-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid | biospider | | trans-Ferulate | biospider | | trans-Ferulic acid | biospider |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C10H10O4 |
|---|
| IUPAC name | (2E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C10H10O4/c1-14-9-6-7(2-4-8(9)11)3-5-10(12)13/h2-6,11H,1H3,(H,12,13)/b5-3+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | KSEBMYQBYZTDHS-HWKANZROSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | COC1=C(O)C=CC(\C=C\C(O)=O)=C1 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 194.184 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 194.057908808 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxycinnamic acids. Hydroxycinnamic acids are compounds containing an cinnamic acid where the benzene ring is hydroxylated. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Phenylpropanoids and polyketides |
|---|
| Class | Cinnamic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Hydroxycinnamic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Hydroxycinnamic acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Cinnamic acid
- Coumaric acid or derivatives
- Hydroxycinnamic acid
- Methoxyphenol
- Phenoxy compound
- Anisole
- Methoxybenzene
- Styrene
- Phenol ether
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Alkyl aryl ether
- Phenol
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Benzenoid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Ether
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | 1.51 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | Not Available | |
|---|
| Melting Point | Mp 174° | DFC |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 8 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | solid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Glentham | GK2300 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | F308895 |
|---|