| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation date | 2015-10-09 22:32:57 UTC |
|---|
| Update date | 2017-01-19 02:36:37 UTC |
|---|
| FoodComEx ID | PC000826 |
|---|
| FoodDB Record | FDB004724 |
|---|
| Chemical Information |
|---|
| Name | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
|---|
| Description | Dimethylformamide is a polar (hydrophilic) Aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such as SN2 reactions. Dimethylformamide can be synthesized from methyl formate and dimethyl amine or reaction of dimethyl amine and carbon monoxide. Dimethylformamide is not stable in the presence of strong bases like sodium hydroxide or strong acids such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid and is hydrolyzed back into formic acid and dimethylamine, especially at elevated temperatures.; Dimethylformamide is the organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NC(O)H. Commonly abbreviated DMF (though this acronym is sometimes used for dimethylfuran), this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Pure dimethylformamide is odorless whereas technical grade or degraded dimethylformamide often has a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Its name is derived from the fact that it is a derivative of formamide, the amide of formic acid.; N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) is a clear liquid that has been widely used in industries as a solvent, an additive, or an intermediate because of its extensive miscibility with water and most common organic solvents. Its health effects include hepatotoxicity and male reproductoxicity, possibly linked with mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) alterations including mtDNA common deletion (delta-mtDNA4977) and mtDNA copy number; during the biotransformation of DMF in the body, free radicals are formed, including hydroxyl radicals.; The world-wide consumption of DMF in 2001 was approximately 285,000 metric tonnes and most of that was used as an industrial solvent. Overexposure to DMF could result in hepatotoxicity, alcohol intolerance, possible embryotoxicity and teratogenicity in humans and animals, and decline of human sperm motility. Based on its wide application and a wide range of toxic effects, DMF has been selected as one of the four priority compounds for human field studies by the National Toxicology Program (NTP) of the US National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). The current permissible exposure limit for DMF in the working environment is 10 ppm in both USA and Taiwan. The concentrations of two major DMF metabolites in urine, N-methylformamide (U-NMF) of 15 mg/L and N-acetyl-S-(N-methylcarbamoyl) cysteine (U-AMCC) of 40 mg/L, were recommended as the biological exposure indices (BEIs) by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists for DMF exposure in workplace. (PMID: 17254560). N,N-Dimethylformamide is found in papaya. |
|---|
| CAS Number | 68-12-2 |
|---|
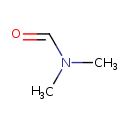
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | Source |
|---|
| Dimethyl formamide | biospider | | Dimethyl-formamide | biospider | | Dimethylamid kyseliny mravenci | biospider | | Dimethylforamide | biospider | | Dimethylformamid | biospider | | Dimethylformamid (german) | biospider | | Dimethylformamide | biospider | | Dimetilformamide | biospider | | Dimetylformamidu | biospider | | DMF | biospider | | DMF (amide) | biospider | | DMF (dimethylformamide) | biospider | | DMF (van) | biospider | | DMFA | biospider | | Dwumetyloformamid | biospider | | Dynasolve 100 | biospider | | Formamide, dimethyl- | biospider | | Formamide, n,n-dimethyl- | biospider | | Formic acid, amide, n,n-dimethyl- | biospider | | Formin acid,amide,n,n-dimethyl | biospider | | Formyldimethylamine | biospider | | HCON(CH3)2 | biospider | | HSDB 78 | biospider | | N-formyldimethylamine | biospider | | N, n-dimethylmethanamide | biospider | | N,n- dimethyl formamide | biospider | | N,n- dimethylformamide | biospider | | N,n-dimethyl formamide | biospider | | N,N-Dimethyl-formamide | HMDB | | N,n-dimethylformamide | biospider | | N,N-Dimethylformamide [UN2265] [Flammable liquid] | biospider | | N,n-dimethylmethanamide | biospider | | N,n-dimetilformamida | biospider |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H7NO |
|---|
| IUPAC name | N,N-dimethylformamide |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C3H7NO/c1-4(2)3-5/h3H,1-2H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Isomeric SMILES | CN(C)C=O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 73.0938 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 73.052763851 |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tertiary carboxylic acid amides. Tertiary carboxylic acid amides are compounds containing an amide derivative of carboxylic acid, with the general structure RN(R1)C(R2)=O (R1-R2 any atom but H). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carboxylic acid derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Tertiary carboxylic acid amides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Tertiary carboxylic acid amide
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physico-Chemical Properties - Experimental |
|---|
| Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Experimental logP | -1.01 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|---|
| Experimental Water Solubility | 1000 mg/mL at 25 oC | ISHOW (NA--) @2ND |
|---|
| Melting Point | -60.4 oC | |
|---|
|
| Foods of Origin |
|---|
| Food | Content Range | Average | Reference |
|---|
| Food | | | Reference |
|---|
|
| Production Data |
|---|
| Production Method | commercial |
|---|
| Production Method Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Production Method Reference File | Not Available |
|---|
| Quantity Available | Production upon request, up to 2 g |
|---|
| Delivery Time | Not Available |
|---|
| Storage Form | liquid |
|---|
| Storage Conditions | -80°C |
|---|
| Stability | Not Available |
|---|
| Purity | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectral Data Upon Request | Not Available |
|---|
| Provider Information |
|---|
|
| Commercial Vendors |
|---|
| Glentham | GK7327 |
|---|
| MetaSci | HMDB0001888 |
|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | HMDB0001888 |
|---|
| Toronto Research Chemicals | D473905 |
|---|